Symphonia globulifera also called boarwood, belongs to the family, Clusiaceae (Guttiferae). The genus, Symphonia includes 17 species.
The plant is widespread in tropical Africa countries such as Tanzania, Madagascar, Nigeria, Gabon, Angola, Zambia Pacific, tropical American countries such as Mexico, Panama, Costa Rica, Mexico, Brazil.
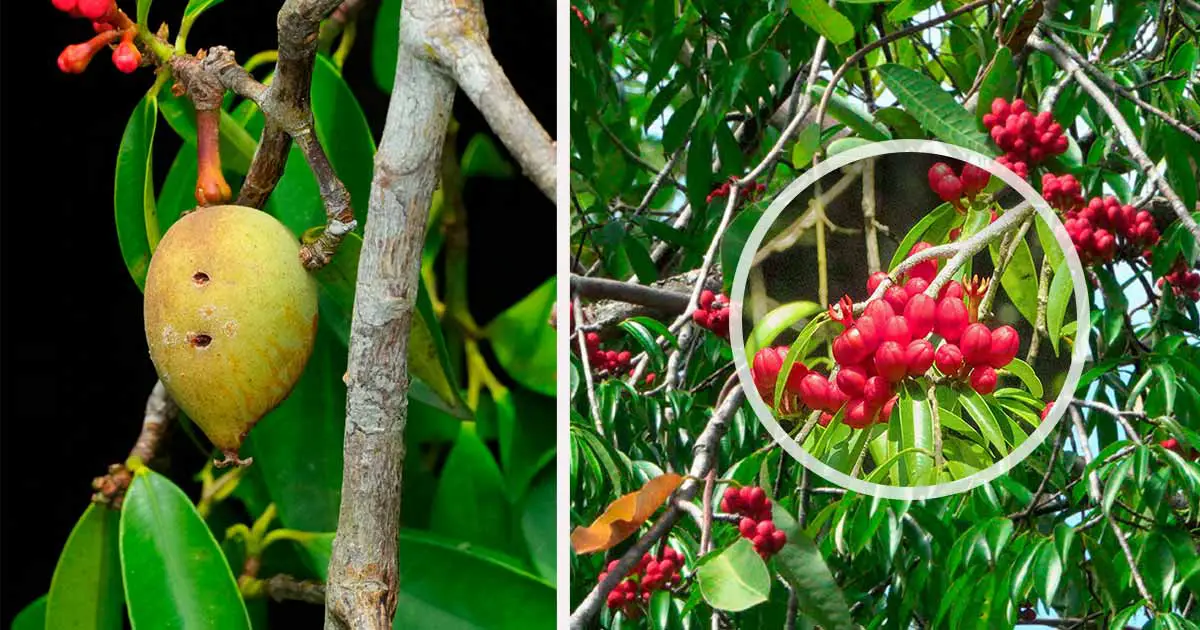
The slow growing tree can grow up to 30 m. It has a long, cylindrical and straight trunk. The trunk also has stilt-like roots at the lower parts. The bark is furrowed. Leaves are opposite, glabrous, lanceolate, or oblong, leathery with blades 5 to 11 cm long.
The red flowers have red staminal column and black anthers, while the fruits are drupes, ovoid, or globular. The seeds are deep red on the inside. Bright yellow sap is obtained in all parts of the plant.
Other common names of Symphonia globulifera include boarwood, chew stick, hog gum, “manil marécage”,“palétuvier jaune”(French Guiana), “anany”(Brazil), “machare”(Colombia), “barillo”(Guatemala, Honduras)
The wood of boarwood are also called manil’, ‘manni’, ‘ossol’ (Gabon) or ‘boarwood’. It is an important source of timber for carpentry, construction, making plywood, canoes, flooring.
The water-insoluble gum from the bark also called ‘hog gum’, ‘mani wax’ or ‘karamani wax’, is used to make glue, candles.
In Ghana, the tonic from the gum bark is used as an appetizer, stomachic, while extract from the bark is used to manage river blindness while in Cameroon, the bark and heartwood is used as a laxative for pregnant women. In Congo, the leaves saps are sniffed to treat nose bleeding. Ugandans use the bark to treat cough.
In Nigeria, the gum can serve as a diuretic and to treat gonorrhea, while leaves decoction are utilized for the treatment of malaria, diabetes, skin diseases. The bark extract serves as an emetic, and the gum used to treat scabies in Gabon.
Traditional healers in Columbia use decoction of the bark of Symphonia globulifera for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. The resin is used to treat wound infection.
READ ALSO: Rosemary Plant (Rosmarinus officinalis): Health Benefits, Dosage, Side Effects
Composition of Symphonia globulifera (Boarwood)
Most of the compounds extracted from the Symphonia globulifera are mainly polycyclic polyprenylated acylphloroglucinols (PPAPs) and xanthone derivatives of PPAPs called oxy-PPAPs. Most of these compounds are from the root extract, while guttiferone A has been observed in the seeds and leaves.
These PPAPs and oxy-PPAPs include guttiferone (A, B, C, D), symphonone (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I), 7-epi-Isogarcinol, 7-epi-Garcinol, 14-Deoxy-7-epi-isogarcinol, and 7-epi-Coccinone B.
There are maclurin, polyhydroxylated polyprenylated xanthones and benzophenones such as Globulixanthone (A, B, C, D, E), globulixanthone, globuliferin, symphonin, xanthone V1, norathyriol, gentisein, globuxanthone, ananixanthone, mbarraxanthone, 1,7-Dihydroxyxanthone, 1,5,6-Trihydroxyxanthone, 1,3,5,6-Tetrahydroxyxanthone, ugaxanthone, and symphoxanthone.
These compounds can be found in either the root bark, seed, leaves, heartwood and twigs of the plant.
Three flavonoids, morelloflavone, GB-2, and GB-3, have been isolated from the leaves and twigs of Symphonia globulifera. Methyl nervonate, a fatty acid, is another compound found in boarwood in Brazil.
The wood of Symphonia globulifera also contains 47–52% cellulose, 24% lignin and 17–20% pentosan.
Health Benefits of Boarwood
Antimicrobial activity:
Compounds from Symphonia globulifera such as globulixanthones C, D, and E have antimicrobial activity against gram-positive organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Vibrio anguillarium, but not against gram-negative organisms. Biflavonoids and xanthones from the stem extract of boarwood are antimicrobial agents.
Antimalarial activity:
Compounds such as polyhydroxyxanthones, oxygenated, and prenylated xanthones, bixanthones and xantholignoids. Prenylated xanthones such as globuliferin, gaboxanthone, symphonin and guttiferone A in the seed shell extracts of S. globulifera.
Guttiferone A has antiplasmodial activity against P. falciparum W2 strains. Other 12 compounds from the bark extracts of S. globulifera also have certain antimalarial activity.
Antioxidant activity:
Compounds such as guttiferone A, and xanthones such as gaboxanthone, globuliferin, and symphonin are antioxidant compounds. The guttiferone A has more radical scavenging properties than the xanthones.
These compounds mop up free radicals that cause diseases such as heart diseases, cancer.
Anticholinesterase activity:
Acetylcholinesterase is an enzyme that hydrolyses acetylcholine to acetate and choline, and helps in the transmission of nervous information.
Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase causes accumulation of acetylcholine and blockage of neurotransmission (this mechanism is important in drug detoxification and Alzheimer’s disease). Guttiferone A isolated from Symphonia globulifera is an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.
Anticancer effect:
Two compounds – Globulixanthone A, and B, discovered from the root bark extracts of Symphonia globulifera have anticancer property against human epidermoid carcinoma of the nasopharynx (KB cell line). However, the mechanism of action is poorly understood.
Antileishmanial property:
Guttiferone A and Xanthone V1 has antiplasmodial activity, but also additional antileishmanial action against Leishmania donovani. The main issue with utilizing the antiparasitic activity is the apparent lack of selectivity and cytotoxicity of the compounds towards the host cells.
Anti-HIV activity:
Boarwood extract has shown in vitro toward HIV infected human cells (CEM‑SS cells). Compounds such as guttiferones A, B, C, and D have been suggested to be involved. However, there is no evidence of decrease in replication of the virus.
Anti-fatty acid synthase activity:
Fatty acid synthase is now a target of diseases caused by viruses, fungi. There are two types: Type I (animal and fungi)and Type II (bacteria and plants). Extract of S. globulifera leaves contain biflavonoids such as morelloflavone, and GB-2, and other compounds with anti-fatty acid synthase activity.
References
- https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Symphonia_globulifera_(PROTA)
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270908738_Symphonia_globulifera_a_Widespread_Source_of_Complex_Metabolites_with_Potent_Biological_Activities