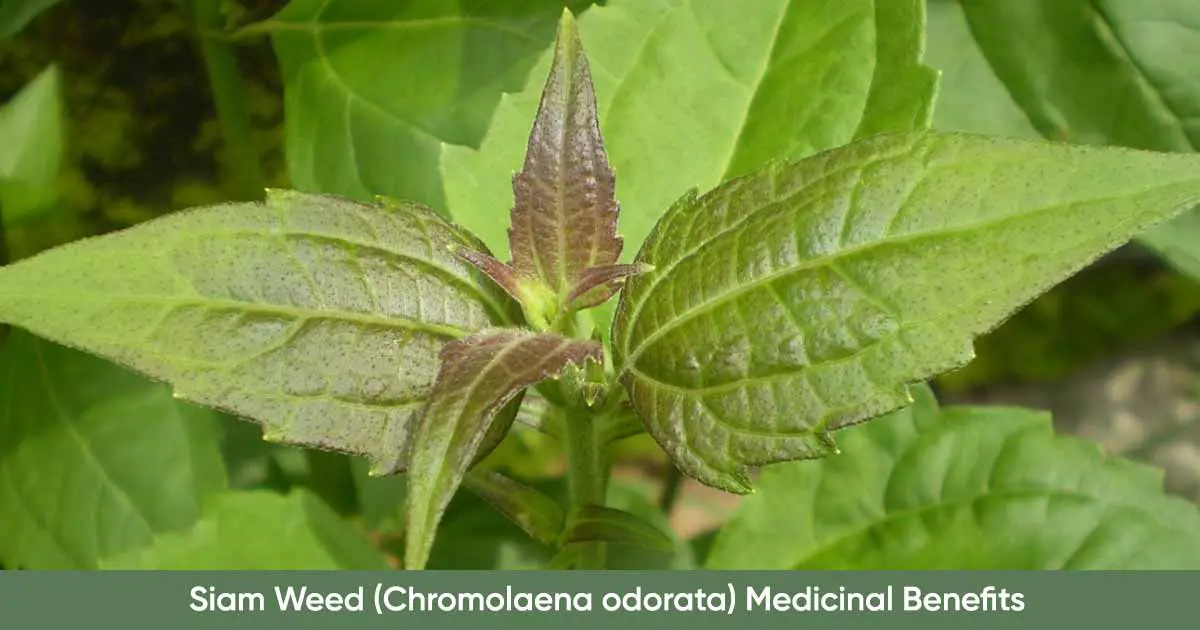
Siam weed (Chromolaena odorata, also called Eupatorium odoratum, Eupatorium conyzoides, Osmia odorata) is a tropical weed belonging to the largest family of flowering plant (Asteraceae). Other names include Jack in the Bush, devil weed, triffid weed, Christmas bush, Elizabeth weed, baby tea, Assam lata, iam-Kraut, agonoi, Obirakara, Olorohuru, independent weed, bitter bush, akintola-ta-ku (Yoruba, Western Nigeria) and ishero (Urhobo, Southwestern Nigeria).
Chromolaena odorata which is related to the Eupatorium spp. is from the Chromolaena genus that contains many species of small herbs, shrubs, found in Asia, tropical Africa, and Europe. Siam weed is an invasive weed that grows in most soil conditions. The scrambling perennial shrub can grow up to 3 to 7 m high.
It has straight, pithy, brittle stems with branches. The leaves are arrowhead-shaped with three veins in a pitchfork appearance, and grow in opposite pairs along the stem. There are many tubular florets appearing in blue, purple, white or pink colors. Seeds are brown-gray to black with pale brown pappus. The leaves give a strong odor when crushed.
Siam weed has anti‑inflammatory, antiplasmodial, astringent, antipyretic, analgesic, antiprotozoal, antitrypanosomal, antimicrobial, cytotoxic, diuretic, antihypertensive activities.
The leaves of Chromolaena odorata has been used in traditional medicine. Poultice from the leaves are used on cuts and wounds for healing. In Vietnam and other countries, the decoction or fresh leaves are used for burns, skin infections, diabetes, leech bites, periodontitis, and soft tissue wounds. The leaf extract is mixed with salt, and serves as a gargle for sore throats and colds.
Constituents
The dried leaf of siam weed contains carbohydrate (31%), crude protein (18%), crude fat (11%), fiber (15%), ash (11%), and moisture (15%).
Chromolaena odorata contains alkaloids, flavonoids, monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes hydrocarbons, saponin triterpenoids, tannins, organic acids, triterpenes/steroids. Other constituents include austrocortinin, cleomiscosin A, D, scutellarein tetramethyl ether, 1,2-methylenedioxy-6-methylanthraquinone, 3-hydroxy-1,2,4-trimethoxy-6-methylanthraquinone, 3-hydroxy-1,2-dimethoxy-6-methylanthraquinone.
- Flavonoids: quercetin, sinensetin, sakuranetin, isosakuranetin, kaempferide, padmatin, kaempferol, betulenol, 2-5-7-3 tetra-o-methyl quercetagetin, tamarixetin, ombuin, salvagenin, two chalcones and odoratin.
- Phenolic acids: p-coumaric, ferulic, vanillic, protocatechuic, p-hydroxybenzoic acids.
- Essential oils: geyren, bornyl acetate and β-eubeden.
- Triterpenoids: ursolic acid
- Phytoprostane compound: chromomoric acid
- Phytosterols: stigmasterol
- Fatty acids: tianshic acid, 3β-acetyloleanolic acid
- Lignans: (−)-syringaresinol, (−)-medioresinol, (−)-pinoresinol
Medicinal Benefits of Chromolaena odorata
Antioxidant effect:
Siam weed (C. odorata) contains phytochemicals such as triterpenes, alkaloids, flavonoids, and biomolecules. These compounds have antioxidant effect (free radical scavenging ability), by boosting antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase.
Antioxidant compounds reduce the oxidative damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS damage leads to lipid peroxidation, DNA damage and enzyme inactivation.
Wound healing:
Extract of Chromolaena odorata has both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect. In wounds treated with the extract, it increased fibroblast proliferation, collagen synthesis and neovascularization, and further increased wound tensile strength. This facilitates wound healing more than untreated wounds.
The mechanism of wound healing could also be through proliferation of dermal fibroblasts, endothelial cells and epidermal keratinocytes.
Anti-inflammatory activity:
Chromolaena odorata iexhibit anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in vivo. It contains compounds with anti-inflammatory activities, such as isosakuranetin and stigmasterol. It reduces the activities of proinflammatory enzymes like cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase, proinflammatory mediators, prostaglandin E2 and nitric oxide, and expression of proinflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β.
Analgesic effect:
Owoyele et al. reported that C. odorata extract exhibit analgesic activity in hot plate latency assay and formalin paw licking tests. It reduced the number of writhings in the acetic acid-induced writhing test.
Spermatotoxic effect:
Studies reveals that the alkaloids from Chromolaena odorata decreases the testes–body weight ratio, concentrations of testicular total protein, glycogen, sialic acid, and cholesterol. It also decreased the activities of γ-glutamyl transferase, acid phosphatase, and alkaline phosphatase, serum LH, FSH levels, testicular and serum testosterone level, sperm count, motility, and density (Yakubu Musa Toyin et al., 2014).
Antidiarrheal effect:
Methanolic extract of C. odorata leaves was used to test for the antidiarrheal effect on the castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice. It reduced the intestinal motility, frequency and wetness of stools (Aba et al., 2015).
Antibacterial activity:
Siam weed inhibit both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria like Bacillus cereus, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Proteus vulgaris, Propionibacterium acnes, V. cholerae. Flavonoids such as scutellarein tetramethyl ether, sinensetin exhibit the antibacterial effect.
Treat skin infections:
Chromolaena odorata is used in Vietnam and other countries to treat skin infections and rashes. The stem extract is used to treat infection caused by Propionibacterium acnes.
Toxicity
Chromolaena odorata is poisonous due to the high level of nitrates, which is 5 to 6 times greater than the level toxic to wildlife. It can cause diarrhea, and death in animals.
The use of Chromolaena odorata is disputed as it contains pyrrolizidine alkaloids which exhibits hepatotoxicity and carcinogenicity activities. It causes allergic issues such as skin problem, asthma in sensitive persons.
References
- https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/mmr.2017.6133
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5414454/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780128000182/toxicological-survey-of-african-medicinal-plants
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350397597_The_Pharmacological_Properties_and_Medicinal_Potential_of_Chromolaena_odorata_A_Review
- https://manoa.hawaii.edu/hpicesu/DPW/chrodo_flier.pdf