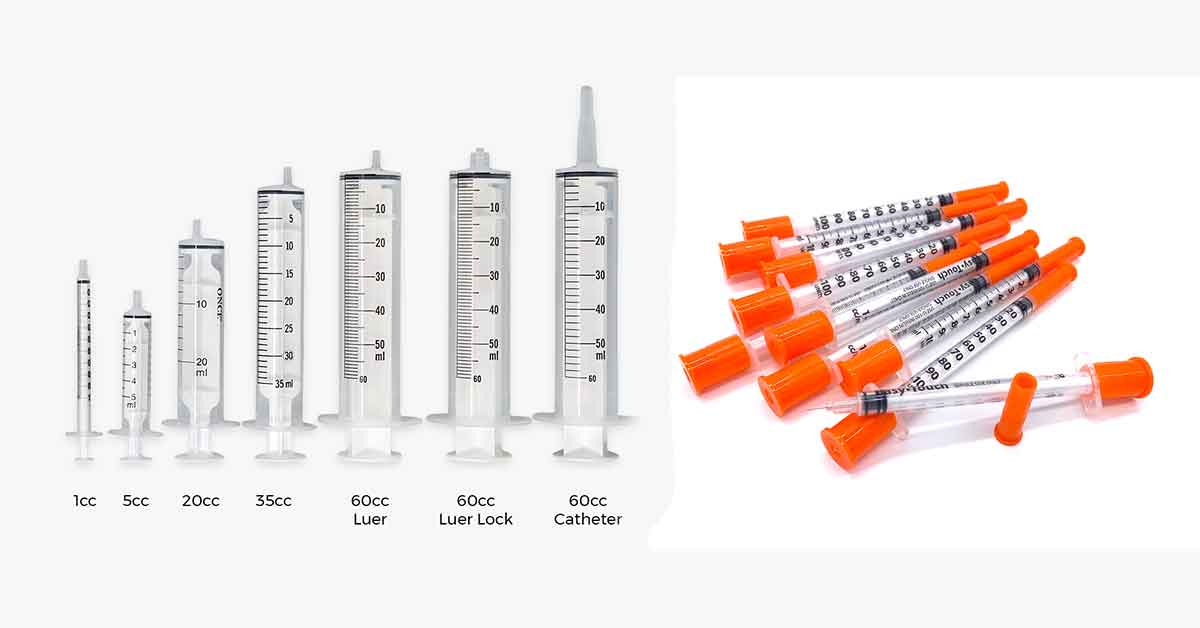
A syringe is a medical instrument used to inject medicines, vaccines, or withdraw fluid from the body of humans and animals. Various types of syringes are made from medical-grade materials, to ensure safety and precision.
Syringes are made from different materials like the plastic, glass, and metal. The plastic material is the most dominant materials in the syringes, however materials like glass and metal were first used historically. They glass and metal material were used, cleaned and reused again.
However, the disposable plastic syringes made of plastic with stainless steel needles are safer as they are disposed after use eliminating the spread of disease.
Though the history of invention of syringes is not clearly known, early report by the UK architect Sir Christopher Wren, showed he administered wine and opium into the veins of dogs in the 17th century. The scientist, Robert Boyle, also used syringe to conduct experiment while investigating gas pressure.
Alexander Wood, a Scottish physician, is credited with inventing the modern hypodermic syringe in 1853 to treat pain in one part of the body. He attached the hollow needle, created earlier by Irish doctor Francis Rynd, to a plunger.
French physician Charles Pravaz also created the hypodermic syringes, at similar time as Alexander Wood. The syringe makes use of a hollow needle to inject substances under the skin and to draw up blood. However, he used the silver material unlike Alexander Wood that used glass material. This made it impossible to control the amount of medicine to be administered. He also did not use plunger like Wood but used a screw.
Alexander Wood used his hypodermic syringe (Fergusson syringe) to inject Morphia, a mixture of sherry and morphine to treat a woman with neuralgia in 1853.
The invention of plastic disposable syringe is the brainwork of Colin Albert Murdoch, a British citizen living in New Zealand in 1956.
Parts of a Syringe
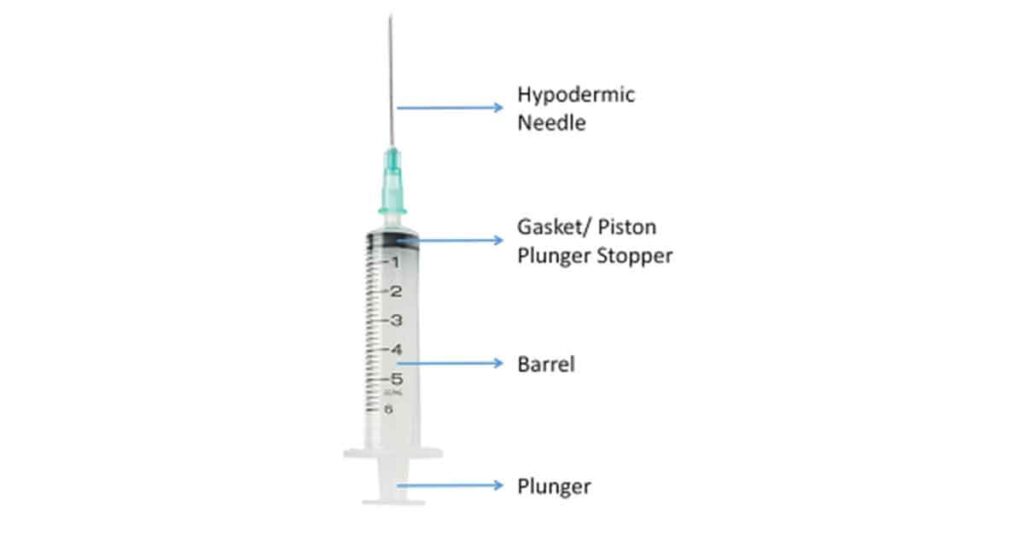
Though there may be variations in different types of syringes, the main parts of syringes are the barrel, plunger and the needle.
The barrel is mostly made of polypropylene material, and has markings showing different measurements according to the milliliter (mL) scale to help the healthcare giver to administer accurate doses. It is the part of the syringe where the medication is held before it is injected. It is usually transparent.
The plunger controls the dosage of injection to be given either through the needle or the connected tube.
The needle is the sharp hollow tube that is used to pierce the skin and inject the medicine. Most needles come with caps to protect the healthcare givers from accidental puncture.
Different types of syringes have different purpose of use. When large volume of medication are to be administered, larger capacity syringes are necessary. The desired pressure flow is another important consideration, with larger capacity syringes having lower pressure flow unlike smaller syringes.
Another consideration during reading the syringe is to measure the plunger’s top ring.
The different types of syringes have different capacity, needle size, needle gauge, and syringe tips.
The size of the needle determines the thickness or thinness of the needle.
Main Indication of Syringes
- To inject medication to the body through intramuscular, intradermal and subcutaneous routes.
- Measure and draw fluids from the body and for biopsy sampling.
- Deliver intravenous therapy directly to the bloodstream.
- Irrigation of wound, eyes, ears, or irrigate catheters for enteral feeding.
Tips for Selection of the Right Syringes
While selecting from the different types of syringes, you should consider the volume of medication, the viscosity of medication which will determine the needle gauge, the site of injection which will determine the needle gauge and needle length.
In selecting the right type of syringe, consider the gauge, length, and use.
Needle gauge:
In choosing the right needle gauge, consider the skin or hide thickness and depth of the injection. The higher the gauge number, the smaller the needle width. However, the smaller the gauge number, the larger the diameter or width. Large diameter gauges with thicker needle walls are durable.
Larger gauge number give less bruising or pain to the patient while lower gauge has stronger needle and lesser chances of breaking or bending.
Most common gauges are 26 and 27, and they can adapt to intramuscular, intradermal, and subcutaneous injections. For intradermal injection, the recommended gauge number is between 26 to 28, 26 to 30 is for intramuscular injection, while 19 to 27 is for subcutaneous injection.
Higher gauge numbers are used for dense skin and for low viscous injection while lower gauge numbers are used for highly viscous injection.
In selecting the needle size, the size ranges from 3/8 inch to 3 1/2 inches. Injection deeper into the skin need longer needles. The length used for intramuscular injection ranges from 3/8 inch to 3 1/2, while intradermal injection requires between 3/8 inch to 3/4 inch. Subcutaneous injection use a needle size range between 1/2 inch to 5/8 inch.
The The 1/2- and 5/8-inch needles are most used lengths for intradermal and subcutaneous injection. Shorter needle length gives less bruising or pain.
Intradermal injection is given at 10 to 15 degree angle in the dermis. Subcutaneous injection is given at 45 to 90 degree angle in the subcutaneous layer while the intramuscular injection is given at 90 degree angle in the muscle just below the subcutaneous layer.
Common Types of Syringes
We have various types of syringes in clinical settings and they include:
Disposable syringes
Disposable syringes are the most used types of syringes. They are meant for single use and comes in sizes ranging from 1 ml to 60 ml. The disposable syringes are used for routine injection, vaccination and extraction of blood.
The Luer Slip syringe
This luer slip syringe is a new technology that has a smooth spigot on the top unlike other types of syringes. It uses a friction-fit connection, unlike other types that use collars or threaded connections. This ensure a seamless and secure attachment. The tip can be easily pushed into the needle hub to ensure a secure connection.
The Luer slip syringe can be a three-part syringe or a two-part syringe. The three part syringe has a barrel, a plunger with a gasket, and a needle, while the two-part syringe has no gasket on top of the plunger.
The gasket in the three-part syringe is made from latex or latex-free rubber. The latex-free rubber is for people having latex allergy. The gasket is to guarantee smooth and effortless movement of the plunger.
Both the barrel and plunger are made from medical-grade polypropylene (PP) as it is more durable, and resist chemical degradation, stress, cracking and fatigue.
Luer slip types of syringes are available in sizes 1ml, 3ml, 5ml, 10ml, 20ml, 30ml, 60ml
The Luer lock syringe
The luer lock syringe is also called three-part syringe has three important parts: the barrel, plunger with gasket and needle. This syringe has an internal thread and a collar on the top. The internal thread allows for tight screw-like connection between the needle and syringe and prevent any movement or separation. It secures the needle in place.
Both the barrel and plunger in the Luer lock syringe is made from medical-grade polypropylene (PP). This material has properties like chemical resistance, durability, resistance to cracking, stress, fatigue, ethylene oxide sterilisation.
Gasket is made from either latex or latex-free rubber. It is used to create an airtight seal between the barrel and the plunger, preventing air entry or leakage, and ensure accurate fluid injection. The gasket also ensure smooth movement of the plunger.
The Luer lock types of syringes are available in sizes like 1ml, 3ml, 5ml, 10ml, 20ml, 30ml, 60ml.
Eccentric Tip
Used to inject directly into the vein. It has an off-center tip, used for surface vein or artery injection. The available eccentric tip sizes are 10ml, 20ml, 60ml.
Insulin syringes
Insulin syringes have finer needles and are used to inject insulin doses in diabetic patients. These types of syringes are ysed to deliver low dose of insulin injection.
Tuberculin syringes
Tuberculin syringes are calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a milliliter, are usd to administer small doses accurately. They are used in the testing and treatment of tuberculosis.
Catheter Syringes
Catheter syringes are used for purposes like drainage and irrigation procedures. It is manufactured with tapered tips end to allow catheters to slip on and off of the tip.
Used to inject and withdraw fluid through a catheter, flushing wounds or when using a slip tip needle that is too large to use standard slip tip syringe.
Toomey or irrigation syringe
This type has wider opening straight tip that fits onto feeding tube, used for wound irrigation. It may have a loop on the plunger to allow for one-handed operation.
Multi-Shot Needle Syringe
It is a special syringe that refills itself after an injection from an inbuilt reservoir giving several doses with the same syringes. However, this type of syringe is rarely used due to contamination.
Safety syringe
A more advanced syringe type used in emergency rooms, and high risk environment where accidental needle-stick injury and risk of blood-borne infection and disease transmission is high.
Dental syringes
Dental syringes are used by dentists to administer anaesthetic solutions. It can also be used to supply water, mist or compressed air to the oral cavity and clean debris in the areas the dentist is working on.
Oral syringes
Oral syringes are mostly used in small children and animals to deliver medications directly to the mouth. The syringes are used as measuring instrument to get accurate dose of medication to be given.
Venom Extraction Syringe
Venom extraction syringe creates a vacuum that sucks out poison from a wound. It is used to venom from wound without the need to puncture the wound
Prefilled Syringe
This type of syringe comes pre-loaded with medication. It is for single use, and ensures medication accuracy as it is already loaded.
Auto-disable Syringe
A type of syringe designed for one-time use only as the plunger locks automatically after the syringe is used which prevents reuse. It is recommended by WHO for immunization as it prevents reuse.
Glass Syringe
Used in situation where precision and purity is important. The glass material can be sterilised and reused. It is ideal for medication that reacts with plastic materials.
Different Sizes of Syringes
We classify most syringes based on the capacity, which is expressed in milliliter (mL) or cubic centimeter (cc), with one milliliter (1 ml) equal to one cubic centimeter (1 cc). The milliliter measurement is used for the liquid volume, but the cubic centimeters is used for the measurement of volume of solids.
The syringe sizes determine the needle gauge and needle size.
Syringe are available in sizes ranging from 0.25mL to 450mL. The common syringes sizes are 1ml, 2ml, 2.5ml, 3ml, 5ml, 10ml, 20ml, 30ml, 50ml, and 60ml.
1 mL or less than 1 mL syringes
1 ml syringe is a versatile and commonly used syringe for tuberculin, diabetes injection, vitamin deficiencies (vitamin K for infant and newborn), post-operative situations, and also intradermal injection. 1 ml syringe with gauge size from 25G and 26G are used in intradermal injection. Tuberculin syringes have greater than half inches of needle length and gauges between 26G and 27G.
For insulin injection, we have three types of insulin syringes to administer the required lower doses of insulin. The needles are not greater than half inches with gauges between 29G and 31G. For insulin dose of 30 units or less, a 0.3 mL syringe is required. A 0.5 mL syringe is used for insulin doses between 31 to 50 units. A 1mL syringe is used for insulin doses between 51 to 100 units.
2 mL to 3 mL syringes
The 2 ml or 3 ml syringes are also commonly used in hospital setting for administering vaccine injection, and for low dose intramuscular and intravenous injections. The needle gauge is between 23G and 25G, while the needle length is dependent on the patient’ age and other factors.
5ml syringe
This syringe can measure doses of medicines up to to 5 ccs. It is used for intramuscular injections, which is given at an angle of 90 degrees. The needle gauge size is between 22G and 23G.
10 mL syringe
When a high volume of intramuscular injection that requires a larger volume of medicine, the 10 ml syringe can be effective. Needle length for intramuscular injection in adult is between 1 and 1.5 inches, while the needle gauge is between 22G and 23G. The injection is given mostly through the cannula.
20 mL syringes
Due to the larger capacity of the 20 ml syringe, it can be used in taking and fusing many drugs in a syringe before injecting them in an infusion giving set. This is then injected into the patient. The injection is mostly through the cannula.
50 and 60 ml syringes
The 50 – 60 mL syringes are normally used with the scalp vein sets (ranging from 18G to 27G) when administering intravenous injections.
The 50 ml syringes is also used for nasogastric and gastroenteral feeding, manual pharyngeal or tracheal suction and for manual aspiration of liquids or gas from the stomach.
Precaution with Use of Syringes
All disposable syringes and needles are for single use only. Reuse can increase the spread of blood borne infection and disease from contaminated syringes, injury or pain.
References:
- https://www.kmedhealth.com/syringe-sizes/
- https://muzamedical.co.uk/blogs/blog/choosing-a-syringe-what-type-of-syringes-are-there-and-which-should-i-use
- https://medcart.com.au/blog/what-are-the-different-types-of-syringes/
- https://www.nms.ac.uk/explore-our-collections/stories/science-and-technology/syringes/
- https://open.lib.umn.edu/clinicalskills/chapter/different-syringe-tips-and-their-uses/
- https://www.vitalitymedical.com/blog/selecting-syringes-and-needles.html
- https://www.linquip.com/blog/types-of-syringes/