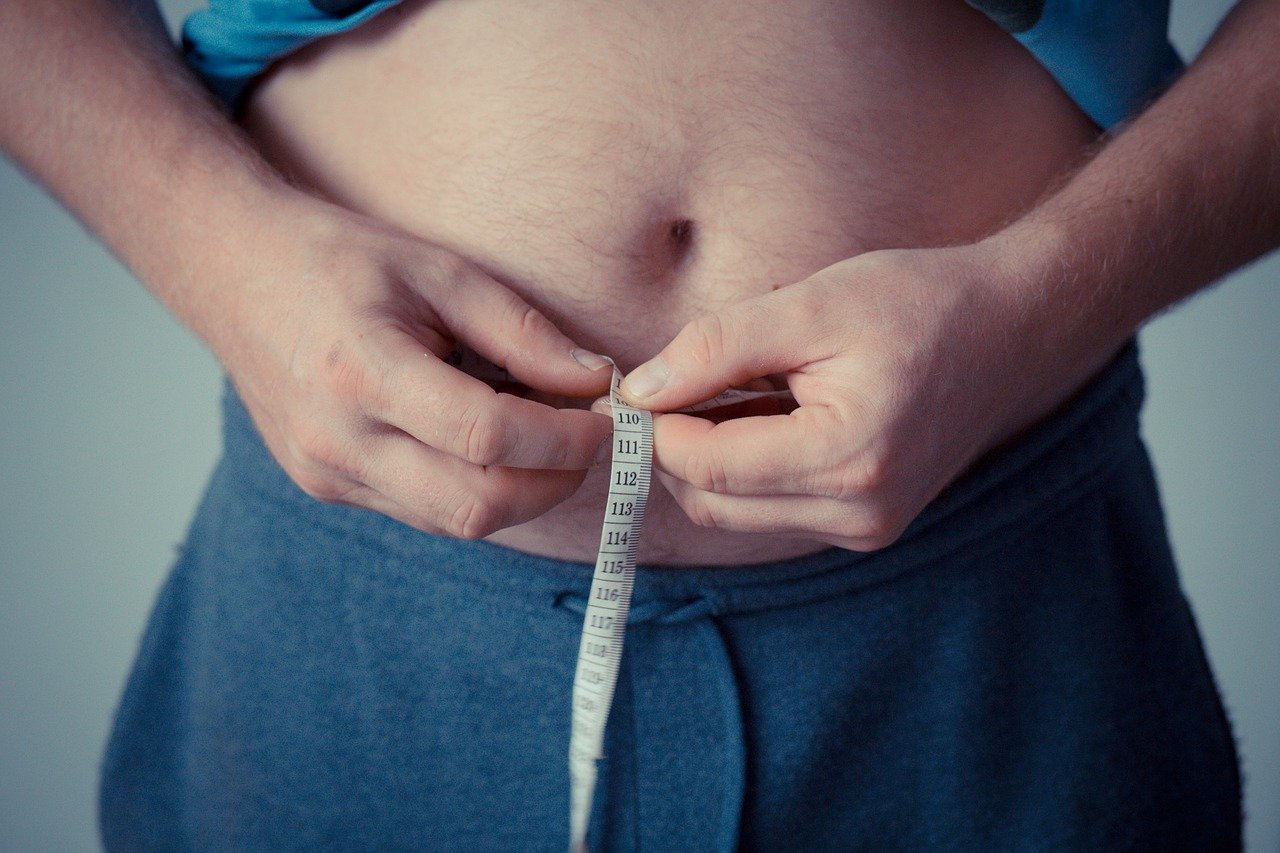
Weight gain can result from an increase in body mass due to excessive exercise, or an increase in body fat due to diet. Weight gain can also result from normal body processes such as pregnancy. Excessive weight gain can cause obesity – a leading cause of type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, stroke, fatty liver disease, heart and kidney diseases.
Drug-induced weight gain is mostly a result of the side effects of certain medications. The chief culprit among them is the insulin and insulin secretagogues used for glycemic control.
Drugs that can cause weight gain
Anti-diabetic drugs
1. Insulin
Insulin does not necessarily cause weight gain but can facilitate it. It is a storage hormone. Glucose is stored in two ways in the body – as glycogen in the muscles and liver, and as fat in the adipose tissue.
If you are insulin resistant, muscles do not take up the glucose, hence the blood sugar level increases. The insulin production by the pancreas will increase in response to the elevated glucose level in the body. This will cause the body to store fat a lot since insulin enhances fat storage.
2. Thiazolidinedione (Insulin secretagogues)
Insulin secretagogues are insulin-sensitizing that reduce insulin resistance in the muscles, liver, adipose tissues. They improve glucose and lipid metabolism. Such agents such as pioglitazone can cause weight gain. This is due to their retention of water and fat accumulation.
A weight-loss diet should be added to the treatment with pioglitazone to avoid this effect. Since metformin does not permit weight gain, a combination of pioglitazone with metformin will limit the side effect of the drug.
3. Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas such as glipizide, glyburide are associated with weight gain. They cause severe hypoglycemia and other cardiovascular symptoms. The weight gain is usually below or within 5kg after 12 months of therapy.
Sulfonylureas should be avoided in obese patients. A combination of glyburide, glipizide with metformin reduces the adverse effect.
Psychiatric therapy
4. Tricyclic antidepressant (TCAs)
Anti-depressants cause weight gain leading to a lack of compliance to medication by patients. Tricyclic anti-depressants such as amitriptyline, imipramine, doxepin cause weight gain during both the acute and long-term treatment of depression.
This weight gain might be a sign of improvement by the patient in some cases. The gain can be as low as 0.4 kg in a month to about 14 to 20 kg in six months in some patients.
5. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs such as sertraline, paroxetine has been associated with initial weight loss during acute treatment followed by weight gain in six months of therapy. Paroxetine has the worst profile in causing obesity.
The mechanism by which anti-depressants cause obesity is not fully understood. It might be due to increased appetite, dry mouth prompting intake of beverages, the sedative effect of the drug which reduces the caloric expenditure of the body.
6. Lithium
The gain in weight, when treated with lithium, is up to 10kg in around 6 to 10 years.
7. Antipsychotic agents
Antipsychotic agents such as olanzapine, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, risperidone can cause antipsychotic-induced weight gain (AIWG). Olanzapine and clozapine are the most likely to cause increased weight gain with ziprasidone causing the least weight gain.
They also impair glucose metabolism, raise triglycerides and cholesterol levels causing metabolic syndrome.
8. Anticonvulsant / antiseizure drugs
This is a common side effect of anticonvulsant drugs such as valproic acid and carbamazepine with weight gain of up to 15 kg during treatment. Newer drugs such as gabapentin and vigabatrin are also implicated.
Weight gain can cause obesity increasing the risk of diabetes and heart diseases.
The mechanism might be due to the stimulation of appetite through the hypothalamus (as a result of lowered blood glucose levels). It may also be due to deficiency of carnitine decreasing fatty acid metabolism and increasing glucose intake.
9. Steroid Hormones
Oral corticosteroids such as prednisolone, dexamethasone are used to treat anti-inflammatory conditions. One of their major side effects is weight gain. This is due to the redistribution of fat to the abdomen and face. They cause retention of fluid and increased appetite.
Read this article on Punch News about how Nigerians use dexamethasone unethically to gain weight
Other steroid drugs such as inhaled corticosteroids (budesonide, fluticasone) used for asthma treatment can cause increased weight gain. Hormonal therapy and contraceptives (estrogen, progesterone) also increase body weight.
10. Beta-Adrenergic Blockers
Beta-blockers such as propranolol, bisoprolol used for the management of hypertension have been observed to cause weight gain. This might be due to due to their decreasing effect on metabolic rate. Older beta-blockers like atenolol, metoprolol are more likely to cause weight gain than newer agents such as carvedilol.
READ ALSO Major differences between the two tetanus vaccines (ATS and TT) you should know