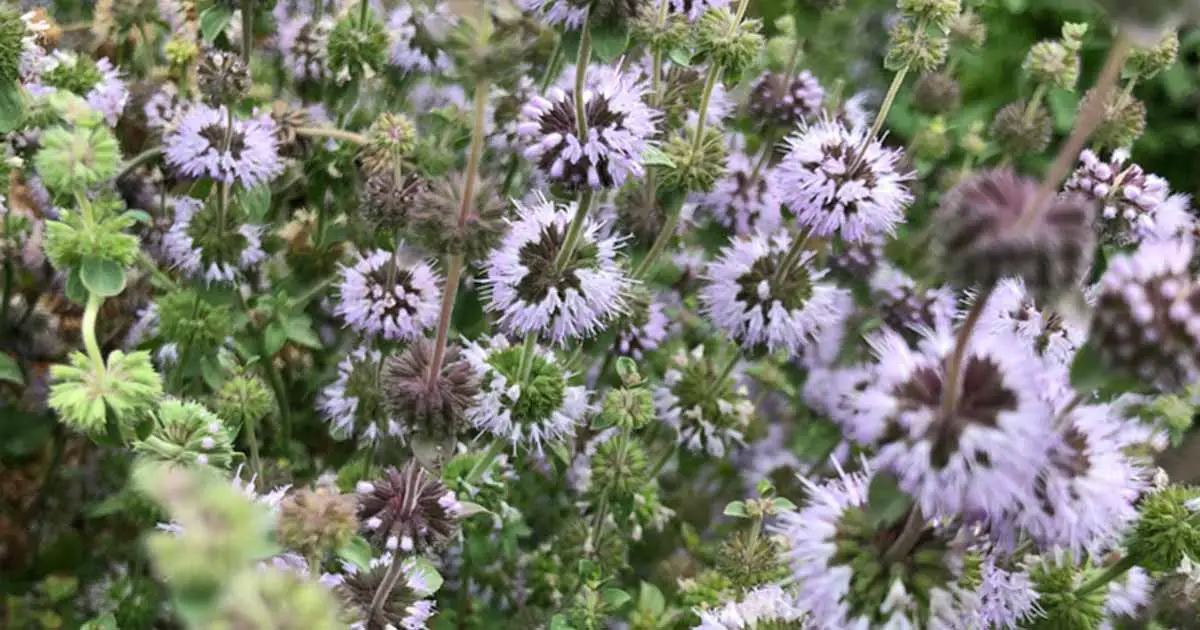
Pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium), also squawmint oil, is a moist-loving flowering plant of the mint family, Lamiaceae. The leaves of the plant emit a strong aroma similar to spearmint. Other names include (European) pennyroyal, or pennyrile, squaw mint, mint pennyroyal, squaw balm, tickweed, grows-in-a-ditch, mosquito plant, and pudding grass.
Mentha pulegium may originate from eastern Mediterranean, Europe, North Africa, Middle East. It is now distributed through western, southern, and Central Europe, Africa, Asia, North and South America, Australia and New Zealand. It grows in damp meadows, around pools, seeps, streamsides, marshes, ditches, and in stream margins.
The annual to perennial plant, which can grow up to 40 cm height, has creeping or erect branched stems. The stem may not have hair or contain hairs with green to red or purplish color. The leaves are opposite, narrowly oval. The small lilac flowers are produced in spikes of whorls.
The plant is used to flavor lamb and tripe in Italian cuisines, and also, a North African dish called Batata fliou. It is also used to flavor detergents, perfumes, and soaps.
The leaves, both fresh and dried, are used in traditional medicine to manage diseases such as influenza, smallpox, abdominal cramps, constipation, hemorrhoids, toothaches, itching, tuberculosis, blemishes to the skin, and to induce sweating.
Constituents of Pennyroyal
Pennyroyal contains essential oils such as piperitone, piperitenone, 4-terpineol, menthone, limonene, naringenin, pulegone, iso-methone, caryophyllene, 1,8-cineole, humulene, chrysanthenol.
Phenolic compounds include rosmarinic acid, ellagic acid, caffeic acid, caftaric acid, chlorogenic acid, m-coumaric acid, o-coumaric acid, p-coumaric acid, cryptochlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, protocatechuic acid.
Medicinal Effects of Pennyroyal
Current medical application of pennyroyal is in the treatment of liver and gallbladder disease, amenorrhea, digestive disorders, gout, colds, and skin disease. It is also used to treat respiratory conditions, cold, and flu. It also has carminative, stimulant, antispasmodic effects.
Insect repellant: The oil from the plant repels fleas, gnats, and mosquitos. Do not use concentrated oil as it can be toxic to humans even at low doses. The essential oil inhibits Tribolium castaneum, Sitophilus oryzae, and Mayetiola destructor.
Antibacterial activity: The essential oils of Mentha pulegium inhibit gram-positive bacteria such Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Mycobacterium aurum, and gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella senftenberg, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Antifungal effect: The essential oils inhibited Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum, Aspergillus sp., Epidermophyton floccosum, enicillium italicum, Rhizopus sp., and Penicillium sp.
Antioxidant effect: Mentha pulegium contain essential oils, phenolic compounds, and gallocatechin, which are powerful antioxidant compounds. They inhibit lipid peroxidation and oxidative damage. It could also serve as a potential food preservative.
Anti-leshmanial effect: The essential oils inhibit the parasitic protozoa: Leishmania major, Leishmania infantum, and Leishmania tropica, which cause leishmaniasis.
Acaricidal effects: Pulegone constituent inhibit house dust mites Dermatophgoidesfarinae and D. pteronyssinus. Mentha pulegium was more effective than other herbs such as citronella, lemon grass, tea tree, and rosemary in fighting the mites.
Hepatotoxic effect: The main constituent in pennyroyal, pulegone, is oxidized by cytochrome P-450 to menthofuran. This pulegone depletes hepatic glutathione by forming electrophilic metabolites. Also, methofuran has direct toxic effect on liver cells (hepatocytes).
The oil cause hepatic and neurologic injury.
Pennyroyal induce abortion: Mentha pulegium plant has an emmenagogue and abortifacient effect. It has compounds that contract the uterine lining, causing the shedding of the uterine lining. The concentrated form such as the oil can cause miscarriage if a pregnant woman takes it.
Most pennyroyal formulations carry a warning label for pregnant women.
Pennyroyal Tea
A herbal tea made from the plant that has mint flavoring. Pennyroyal tea is used to treat cold relief, coughs, fevers, headaches, indigestion, liver, and kidney problems.
The tea is less toxic than the oil, as it has less concentration of the harmful chemical. It is made from boiling the leaves of the plant in hot water. This tea is to be taken once in a while, as it may be harmful to consume regularly. Do not give pennyroyal tea to children as it cause death in infants and children.
Pennyroyal tea induce menstrual flow with less side effect. The tea is also helpful in regulating menstrual cycle and for women who suffer from cystic ovary syndrome.
Pennyroyal Toxicity
Pennyroyal oil is toxic to humans. The toxicity depends on the amount ingested. This toxicity is caused by cyclohexanone pulegone, which makes up 80% to 90% of the constituent of pennyroyal oil. Pulegone gives Mentha pulegium the peppermint flavor. When pulegone is ingested, the liver breaks it down to form metabolites such as menthofuran, piperitenone, piperitone, and menthone. These metabolites cause harmful damage to the body system.
Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and dizziness, occurs when a small volume is ingested. If large volume is ingested, it could lead to the failure of multiple organs in the body, low blood sugar, blood clotting, acidic blood pH, GI hemorrhage, lung congestion, mental status changes, brain swelling, seizures, and possibly, death.
Contraindication
Do not use pennyroyal during pregnancy or lactation, in persons with liver or kidney disease, and for children and infants.
Antidote for Pennyroyal Toxicity
There is no specific antidote for pennyroyal toxicity. However, some treatments such as:
- Administration of gastric lavages
- Emetics, or vomiting inducers
- Use of N-acetylcysteine, as in paracetamol toxicity, since glutathione depletion modulate liver toxicity.
- Use of absorbents like activated charcoal
- Inhibitors of cytochrome P450, like cobaltous chloride or piperonyl butoxide may block pulegone toxicity. This study is yet to be applied to humans.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mentha_pulegium
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/mentha-pulegium
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321061784_Mentha_pulegium_Medicinal_uses_Anti-Hepatic_Antibacterial_Antioxidant_effect_and_Analysis_of_Bioactive_Natural_Compounds_A_Review
- https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/integrative-medicine/herbs/pennyroyal