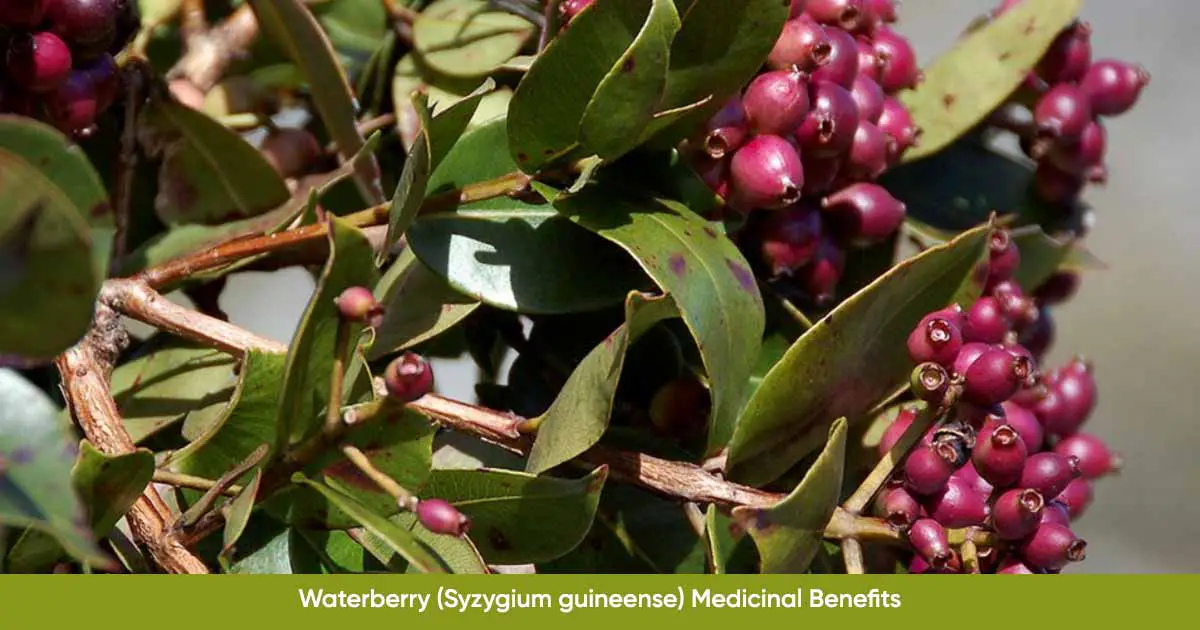
Syzygium guineense, also called ‘water berry, woodland waterberry, waterpear, waterpeer, umdoni (isiNdebele), is a large, evergreen flowering plant from the genus Syzygium, and family, Myrtaceae. The small tree produces edible fruit. It is widely distributed in South Africa, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Central Africa.
The tree is a medium-sized to large evergreen tree with a smooth greyish-white single stem, and purplish-red young leaves. It can grow up to 20 m height. The bark is smooth and greyish-white to grey-brown when young, but turns rough, flaky, creamy, light grey, dark brown or black when matured.
The leaves are simple, opposite, elliptic to lanceolate with smooth margins, when young, but turns to yellowish-green to glossy dark green on the upper surface and paler green and dull under when older. Flowers are creamy white with sweet fragrance. The edible fruit has a single round seed, and are dark purple when mature.
In traditional medicine, the decoctions from the bark is used as a purgative, anthelmintic, antituberculosis, anticancer and treatment of chest ailment, stomach-ache, diarrhoea and malaria. The root and stem extract are used to treat stomachaches and infertility. Leaf extract is used to treat Intestinal parasites, stomachache, diarrhea, and ophthalmia.
Constituents
The plant extract of Syzygium guineense contains sugars, proteins, lipids, terpenoids, alkaloids, triterpenes, flavonoids, anthraquinones, tannins, glycosides, saponins, and phenols. Other compounds include triterpenoids (6-hydroxyasiatic acid, oleanolic acid and ursolic acid).
Major compounds in the leaf are tetratriacontane; 9-octadecanoic acid, n-hexadecenoic acid, and tetratriacontane.
The essential oils contain caryophyllene oxide, δ-cadinene, viridiflorol, epi-α- cadinol, α-guaiene, α-cadinol, cis calamenen-10-ol, citronellyl pentanoate, β-caryophyllene and α-humulene.
Medicinal Benefits of Waterberry (Syzygium guineense)
Syzygium guineense leaf extract has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, antibacterial, antidiarrheal, and antihypertensive activities.
Antioxidant effect:
Syzygium guineenseextracts exhibited significant scavenging and antioxidant properties, due to the presence of phenolic compounds such as polyphenols, flavonoids, and flavonols.
The leaf extract exhibit antioxidant effect against ferric nitriloacetate-induced stress in the liver, heart, kidney, and brain tissues of Wistar rat homogenates. It inhibits the lipid peroxidation and restored the enzymatic and non-enzymatic activities (Nzufo et al., 2017).
Antiplasmodial activity:
Syzygium guineense crude leaf extract showed dose-dependent schizontocidal activity in both the repository and curative tests, and suppresssed the malaria parasite, Plasmodium berghei in mice. It also prevented weight loss, and improved the survival rate (Solomon Asmamaw Tadesse & Zewdu Birhanu Wubneh, 2017).
Constituents in the leaf such as alkaloids, terpenoids, and phenols play important roles in preventing plasmodial infection.
Antidiabetic effect:
The methanol extract of Syzygium guineense leaves exhibit antihyperglycemic property in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. It enhanced the glucose clearance, and increase in hepatic glycogen content. It improved the antioxidant levels, and reduced serum albumin, creatinine, liver enzymes, total bilirubin, serum cholesterol, triglycerides (Ifeoma Chinwude Ezenyi et al., 2016).
The mechanism of action is thought to be through inhibition of alpha glucosidase, free radicals scavenging, and increase intrahepatic glucose uptake and storage.
Anti-inflammatory activity:
The ethanolic extract of S. guineense ethanol leaf exhibited significant anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects on the writhing test at a concentration of 1000 mg/kg in rat models (IOR et al., 2012).
Antidiarrheal activity:
Syzygium guineense ethanol leaf extract exhibited antidiarrheal activity in mice by inhibiting the intrinsic small intestinal propulsion and itopride-induced propulsive activity (Ezenyi & Igoli, 2018)
Antibacterial activity:
Triterpenes, such as 6-hydroxyasiatic acid, oleanolic acid and ursolic acid exhibit antibacterial activity against bacterial strains of Salmonella E., Shigella D., Shigella F., E. coli and Enterobacter.
Anticancer property:
Isolated phytosterols from the stem bark of the Syzygium guineense such as β-Sitosterol and betulinic acid reduce carcinogen-induced cancer of the colon.
The plant extract exhibit anticancer activity against triple-negative breast cancer and colon cancer cells by inhibiting Wnt-signaling and proliferation of Wnt-dependent tumors (Koval et al., 2018).
Toxicity
The bark of Syzygium guineense may be poisonous and could possibly result in death.
References:
- https://bmccomplementmedtherapies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12906-016-1538-6
- https://www.phytojournal.com/archives/2019/vol8issue3/PartF/6-6-98-836.pdf
- https://pza.sanbi.org/syzygium-guineense
- https://www.phytopharmajournal.com/Vol5_Issue4_06.pdf
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/fsn3.2797
- https://pza.sanbi.org/syzygium-guineense
- https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Syzygium_guineense_(PROTA)