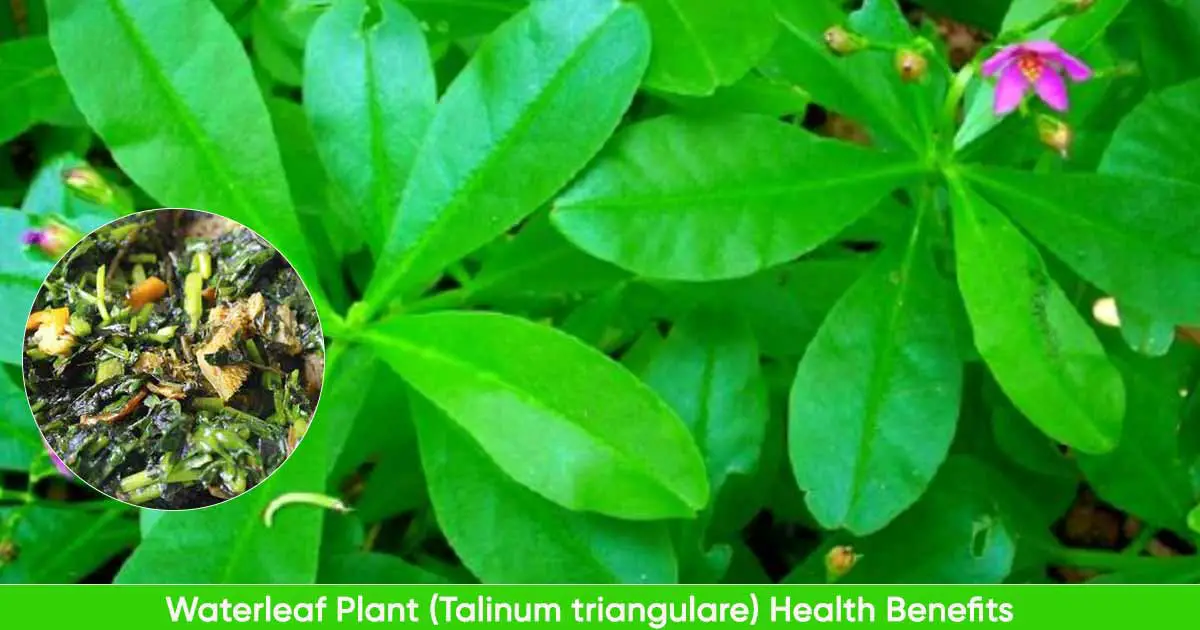
Waterleaf plant (Talinum triangulare (Jacq.) Willd) is a vegetable crop from the purslane family, Portulaceae. The plant is native to Africa, Asia, Central and South America. Waterleaf has a short lifespan and takes between 30 and 45 days from planting to harvest. Waterleaf plant should not be confused with Talinum fruticosum, a closely related plant native to Mexico, the Caribbean, West Africa.
Waterleaf plant is an erect, glabrous, and perennial herb. The roots are swollen, hairless, while the stem light green, smooth, succulent and can grow up to 3 to 10 feet (ca. 3 m). The stem branches have two lateral buds.
The leaves of waterleaf are succulent and edible. The blades are spoon-shaped and may be indented at the apex. Waterleaf produce pink flowers. The fruits are light-green, ellipsoid capsules, dehiscent with many dark brown seeds that open up. These fruits ripen two weeks after flowering.
Waterleaf plant can be propagated by seeds or vegetative cuttings. Even though, the plant can survive wide range of soil, temperatures conditions, they grow best in a temperature ranges of 68 °F (20 °C) to 95 °F (35 °C).
The plant resists pests and diseases, but biopesticide control using Azadirachta indica (neem extract) can be helpful.
Other names of waterleaf are Ceylon spinach, Surinam purslane, Philippine spinach, Grassé grand pourpier, Blatt-ginseng, Lustrosa-grande, Espinaca de Java, and Sweetheart. Local names of waterleaf plant in Nigeria are Mgbolodi in Igbo, Ebe-dondon in Edo, Gbure in Yoruba, Mmommong Ikong in Ibibio.
After harvesting, the plant should be stored in plastic bags and refrigerated at a temperature of 61 °F (16.11 °C) to 66 °F (18.89 °C) to improve the shelf life.
Nutritional Content in Waterleaf
Waterleaf plant contains crude proteins, lipids, Omega-3 fatty acids, moisture, essential oils, amino acids, dietary fiber, minerals such as calcium, potassium, sodium, iron, zinc, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamins such as ascorbic acid, alpha-tocopherols, beta-tocopherols.
The moisture content is as high as 90% of the plant constituent.
| Nutrient | Quantity |
| Carbohydrates | 55.34-56.54% |
| Proteins | 28.82-32.22% |
| Crude fiber | 8.50-9.30% |
| Dry matter | 19.55-23.15% |
| Nitrogen-free extractives | 1.38-2.18% |
| Minerals | Quantity (mg/100g of the plant) |
| Calcium | 74.60 |
| Magnesium | 70.40 |
| Zinc | 10.50 |
| Phosphorus | 196.50 |
| Iron | 0.65 |
| Sodium | 80.60 |
| Potassium | 156.60 |
| Copper | 0.12 |
Phytochemicals in Water leaf
The plant contains alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, tannins, phlobatannin, anthraquinones, steroid, terpenes, phenols, lignans, phytosterols, allicins, cardiac glycosides.
The alkaloids and phenols are the most abundant of the bioactive elements in the waterleaf plant.
The individual constituents are carotenoids (carotene and lycopene), flavonoids (quercetin and kaempferol), benzoic acid derivatives (ferulic acid and vanillic acid), alkaloid (Indicine-N-oxide), hydroxycinnamates (p-coumaric acid and caffeic acid), lignans (retusin), phytosterol (Sitosterol), glycosides (arbutin), saponins (avenacin-B1), and allicins (diallyl thiosulphinate).
Health Benefits of Waterleaf Plant
The bioactive elements in waterleaf plant such as allicins, quercetin, kaempferol, β‐carotene, etc. have anti-cancer, blood pressure lowering, antimicrobial, antioxidant, neuroprotective, antidiabetic effects among others. Some health benefits of waterleaf plant are in:
Weight loss: Due to the high fiber content, the plant can help obesity and accumulation of fats.
Lowers cholesterol levels: In a study with hypercholesterolemic rats, methanolic leaf extract of Talinum triangulare, restored elevated serum lipid profile such as total glyceride, total cholestrol, low-density lipoprotein, and MDA to normal.
Dietary fiber also prevents absorption of cholesterol level from the gut, protecting the body from cholesterol related diseases.
Antioxidants: The plant contains flavonoids, vitamin C and other phenolic compounds that prevent oxidative damage to cells in the body causing cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer. It prevents oxidative stress, and also improve the antioxidant defense system.
Diabetes: Fiber is a non-digestible carbohydrate, that helps to slow down digestion and conversion of starch to sugar. Eating food with high fiber content like waterleaf plant can improve blood glucose control.
Laxative: Dietary fiber and antioxidants can act as a mild laxative. It is used in constipation.
Improves brain function: An experiment using the aqueous leaf extract of Talinum triangulare on Swiss albino mice for 14 days. There was a dose dependent reduction in Malondialdehyde (MDA) activities in the treated mice, which suggests waterleaf plant inhibit oxidative stress, thus preventing neuronal injury. This may enhance the cognitive ability.
Aids digestion: Waterleaf plant has constituents such as dietary fiber that protects the body against gastrointestinal conditions such as indigestion, constipation, flatulence and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Prevent anemia in pregnancy: In some localities, the plant is recommended in pregnancy, as it has micro-elements and nutrients that may help to prevent anemia. It may also improve blood production and clear bilirubin from blood.
Improve liver function: Methanol extract of Talinum triangulare at certain doses suppressed oxidative damage in the liver cells in experimental rats. From the liver function test results, there was decrease in serum hepatic marker enzymes.
Cancer: Waterleaf contains compounds such as squalene, lycopene that prevents cancer forms such as breast, colon cancers.
Other Uses of Waterleaf
Waterleaf is a natural pigment that can be used as colorant in foods. The leaf extract can serve as
inhibitors of mild steel corrosion in acidic medium.
It is also used in bioremediation for accumulating heavy metals from soil exposed to anthropogenic activities. Water leaf extract is also used to broiler chick’s immunity against virulent Newcastle disease virus.
Side Effects of Waterleaf
Water leaf should not be taken raw in large quantities as it contains soluble oxalate, which may increase the risk of kidney stone. It also contains a small quantity of hydrocyanic acid content (cyanide content is lower than the dose range of 50–300 mg/kg of body weight)
Cooking the leaves reduces the oxalates by 50%, and also the nitrates and nitrites. Because of the antinutrients, do not use waterleaf in infant foods.
How to Make Waterleaf Juice
Water leaf juice is filled with phytochemicals and nutrients that help the body in preventing diseases such as diabetic, high blood pressure, cancer. Also, it is used to treat measles in children.
To make a water leaf juice:
- Chop the leaves and stem of the plant into pieces.
- Put them in a blender and add a liter of water.
- Sieve out the chaff after blending, and you are left with a dark green liquid.
- It’s advisable to drink the juice after blending, as refrigerating may affect the levels of nutrients and phytochemicals.
How to Cook Waterleaf Plant
Water leaf should be cooked at low heat for a short period of time, like 5 minutes, to avoid denaturing and loss of nutritional and health value. The slimy vegetable can be sun dried before cooking to retain the dry matter.
Wash the water leaf young stem, leaves thoroughly. You can stir-fry and use in vegetable soups (ofe mgbolodi, edikaiko, gbure, afang soup), sauce and stews with other ingredients such as pepper, onions, meat, chicken.
Waterleaf vegetable soup is made with the leaves and young shoots, and other leaves such as fluted pumpkin leaves, orchorus (jute) leaves, and gnetum africanum (okazi leaves). The soup is popular among the Igbos, Yorubas, Ibibios, Efik in Nigeria.
References
- https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/HS1434
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341182634_Review_on_the_Medicinal_Potentials_of_Waterleaf_Talinum_triangulare
- https://www.idosi.org/gjbb/gjbb8(2)13/3.pdf/26572307_Waterleaf_Talinum_triangulare_Enhances_Cerebral_Functions_in_Swiss_Albino_Mice
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5096282/