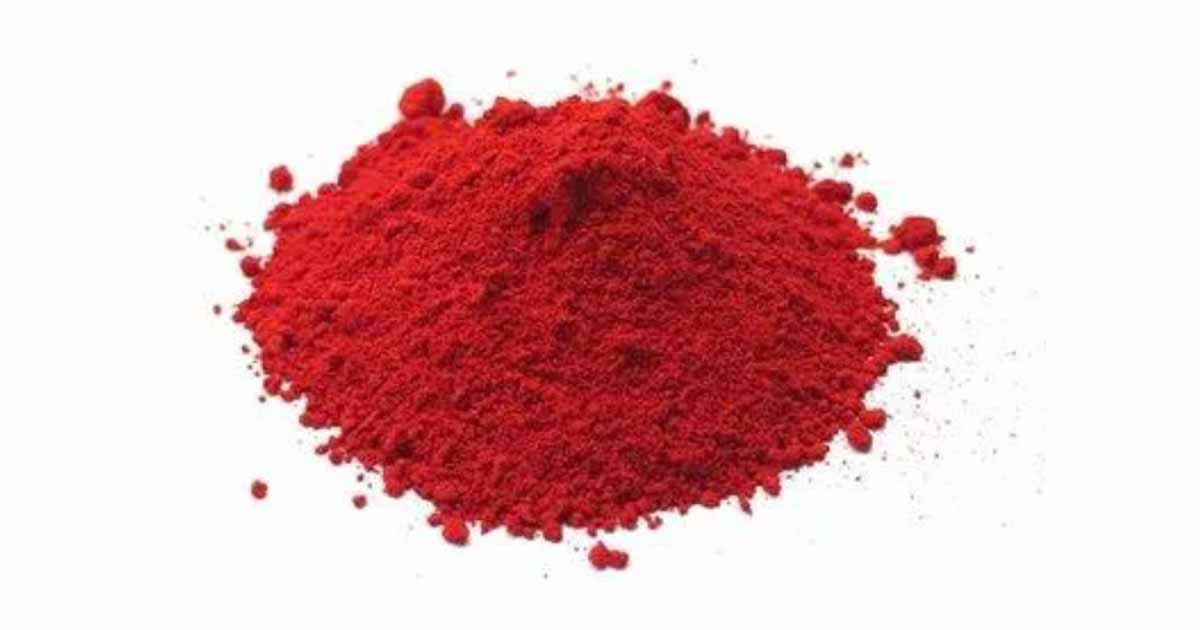
Camwood (Baphia nitida), also called African sandlewood, barwood, or Osun is a perennial shrub belonging to the Fabaceae (Leguminosae). It is widely distributed in the rainforest, secondary forest and abandoned farmland of the coastal region of West Africa (Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Cote d’voire)
Baphia nitida is a small to medium-sized shrub that can grow up to 5 m height. The shrubby red hard wood is heavy and durable. It has a smooth, dark glossy green leaves that are oval-shaped. The attractive white pea-like flowers are fragrant with yellow center. The fruits are made of almost spiral, compressed pod, pointed at each end with 1-4 brown disc-shaped seeds. The seeds are edible.
Camwood is also called Osun, Irosun, Urosun in Yoruba, Aboshi, Ufie in Igbo, Otua, Ositua in Edo, Bois de cam, bois rouge in French.
Camwood dye is a red paste from Baphia nitida. Camwood has been used in traditional medicine to treat stiff joint, rheumatic pain, ringworm, sprains, constipation, wounds, jaundice, ulcers, boils, gastrointestinal issues, skin and venereal diseases.
The ground root bark is mixed with honey for asthma, while the ointment from the powdered heartwood is mixed with shea butter for stiff and swollen joints, sprains and rheumatic complaints. The leaves of Morinda lucida are used with camwood in the treatment against female sterility and painful menstruation.
In the market, the camwood is available as pellets or powder. The powder is pale brown when fresh, but turns dark red or orange on exposure. It is obtained from the core of the Baphia nitida plant after peeling the bark. It has a fibrous texture.
Constituents of Camwood
Camwood dye contains isoflavonoid-flavonoid dimers santalins A and B and santarubins A, B and C. There are other compounds that may contribute to the coloring effect such as baphic acid, baphiin, deoxysantarubin, homopterocarpin, maackiain, pterocarpin and santal.
The leaves contain flavonoid glycosides, saponins, and true tannins. The leaves also contain crude protein, crude fiber, ether extract, ash, lignin, cellulose, and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, and copper.
Health Benefits of Camwood (Baphia nitida)
Antioxidant effect:
Findings by Akande et al., and Bello AM et al., shows that the extracts of Baphia nitida leaves have antioxidant and radical scavenging effects due to the phenolic compounds and flavonoids content.
Benefit to skin:
Camwood powder has antiseptic and skin balancing effect.
It has skin benefits such as in removal of wrinkles, blemishes, eczema, acne, sunburn, rashes, dark spots, improving skin texture, elasticity and tone, and delay ageing. It may also be mixed with rose water, banana, honey, lime, lemon, aloe vera, shea butter, coconut oil. Camwood is used as a face scrub, or for exfoliation.
Camwood is a major constituent of black soap and herbal soaps formulations, together with turmeric and other ingredients
Anti-inflammatory effect:
The leaves of Baphia nitida when formulated as an ointment, showed a dose-dependent anti-inflammatory activity against croton oil and heat induced inflammation on ears of mice and depilated backs of rats. This could be attributed to the rich flavonoid content (N D Onwukaeme, 1995).
Antimicrobial activity:
Extract of camwood dye has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities against Gram positive and Gram negative microorganisms, such as B. cereus, S. aureus, E. coli, P. vulgaris, while P. aeruginosa has lowered inhibition (Olowosulu and Ibrahim, 2006). The activity may be attributed to the presence of secondary metabolites such as alkaloids, and flavonoids.
Antidiarrheal property:
Baphia nitida reduced the severity of diarrhea in castor oil-induced diarrhea test using mice and rats. It reduced the number and weight of wet stools, however, there was no significant effect on intestinal fluid accumulation and gastric emptying.
The antidiarrheal effect may be due to interference with the l-arginine nitric oxide pathway and synergistic with antagonistic action on muscarinic receptors (O. O. Adeyemi et al. 2008).
Analgesic effect:
The extract of camwood shows a dose dependent antinociceptive (analgesic) activity in mice. A 500 mg/kg extract compares with the 300 mg/kg of acetylsalicylic acid in terms of analgesic activity.
References
- https://www.nparks.gov.sg/florafaunaweb/flora/1/7/1717
- https://forestcenter.iita.org/index.php/2019/06/21/baphia-nitida/
- https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajb/article/view/102104/92148
- https://buk.edu.ng/college/bms/journal/articles/article5.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18276093/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7650950/
- https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Baphia_nitida_(PROTA)