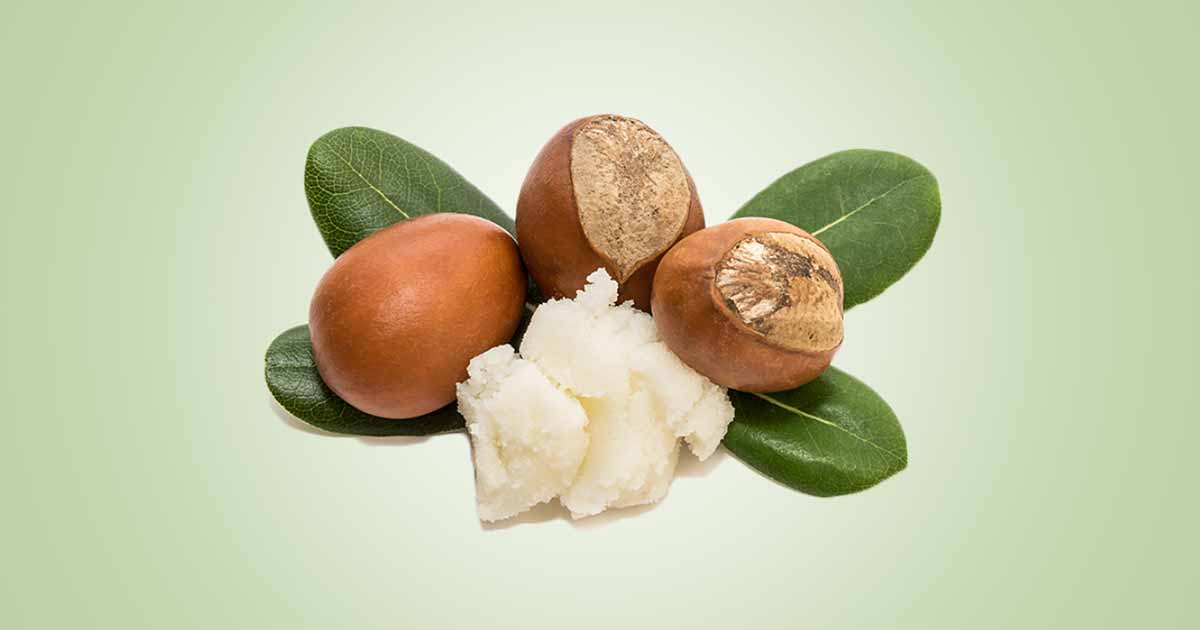
Shea butter is a solid fatty oil from the nuts of shea (Karite) tree, a deciduous plant from the Sapotaceae family. The plant also called Vitellaria paradoxa or V. nilotica, grows in the sub-saharan savannah belt stretching across West and Eastern Africa.
The tree can grow up to 25 m height. It has a spreading crown. The leaves are oblong and clustered at the end of the branches, while the flowers are white and clustered at the end of the shoots. The fruits are green oval, round, and flat with four shiny brown seeds. The fruit has green epicarp, a fleshy pulp or mesocarp and a hard shell or endocarp which encloses a shea kernel or embryo.
The fresh seed kernel has a white, odorless high quality vegetable fat called shea butter. Stale seeds produce dark, and tastes bitter. The bark of the plant is corky, and yields reddish latex.
Other names of shea butter are Butyrospermum parkii (former botanical name meaning butter seed”), shea, shi.
The extraction of shea butter could be through the traditional, the semi mechanized, and the fully mechanized methods. The traditional method is the most commonly used method, but has lower extraction rates when compared to other methods. It involves steps like breaking, roasting, pounding, grinding, kneading, and boiling the shea butter kernel.
In traditional medicine, shea butter is used for swellings, bruises, wounds, dermatitis, skin conditions, nasal congestion, rhinitis. Leaf extracts are used for stomach pain and headache. Bark extract are used for dysentery and to stimulate lactation. The ground bark and root are used for diarrhea, jaundice, and stomach ache.
In the food industry, shea butter has uses in baking, in pastries and confectionery. It is also a cocoa butter substitute in chocolate manufacture as they have similar melting point, high di-stearin amount, and some stearo-palmitine content. The pulp is edible and could also be used to make jams.
Constituents in Shea Butter
Shea butter pulp (100 g) has estimated 74.2% moisture, 179.5 kcal of energy, 22.6 g of carbohydrates, 5.2 g of proteins, 42.2 g of crude fiber, 1.3 g of lipids, and 5.1 g of ash. The kernel contains 30.9 g of carbohydrates, 45.2 g of lipids, 8.1 g of proteins, 9.1 g of crude fiber, and 2.5 g of ash. The sugars include glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
Shear butter pulp also contains high potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus. Other minerals include sodium, iron, manganese, copper, and zinc. Vitamin C is of high quantity, while vitamin B is also found. The vitamin C content is comparable to the levels in oranges.
The pulp also contains amino acids such as aspartic acid, serine, threonine, glycine, glutamic acid, proline, valine, alanine, leucine, tyrosine, cysteine, methionine, valine, lysine, histidine, and arginine.
Shea butter is a triglyceride fat with mainly stearic acid and oleic acid. It has large unsaponifiable fraction that contains bioactive compounds, mostly triterpene alcohols. There are also hydrocarbons, sterols, and other minor components such as tocopherols or vitamin E, and catechins (Alander, 2004).
The saponifiable triglyceride fraction is 90% by mass of the butter and is mainly stearic and oleic acids and smaller quantities of palmitic, linoleic and arachidic acids (Davrieux ve ark., 2010).
Shea butter has a larger amount of saturated fatty acids when compared to olive oilhttps://pharmchoices.com/major-functions-of-vitamin-c-in-the-body/, canola oil, and grape seed oil, which are all liquid at room temperature. The latex contains carotene.
Main Benefits of Shea Butter Benefits
Anti-inflammatory activity:
Shea butter contains cinnamic acid derivatives which inhibit Inos, Cox-2, and cytokines through the Nf-Kb pathway in LPS-activated J774 macrophage cells (Verma ve ark., 2012).
This dominant triterpene (α-amyrin) when combined with β-amyrin shows a dose-related antinociceptive effect against visceral pain (Otuki ve ark., 2005a). It causes a decrease in tissue IL-1β levels, edema formation, and the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocyte.
Cholesterol lowering:
Shea butter lowers low density lipoprotein(LDL) and total cholesterol, which signifies anti-hypercholesterolemic effects. Saponins are present in the unsaponifiable fraction of shea butter. It lowers cholesterol levels by forming mixed micelles with cholesterol and bile acids in the intestine.
Effect on protein metabolism:
Shea butter reduce serum, hepatic and renal tissues’ protein concentration when administered. The effect could be due to saponins, which reduce protein digestibility.
Anti-allergic effect:
Shea butter and Brazil nut are related. Brazil nut cross-reacts with fruits like walnut, almond, peanut and hazelnut. However, shea butter does not share any allergic reaction after topical or oral use. This is probably due to absence of IgE-binding soluble proteins (Chawla ve ark., 2011).
It contains triterpenes such as parkeol, germanicol, butyrospermol, lupeol, dammaradienol, and α, and β-amyrins, 24-methylene-dammarenol, that can suppress hypersensitivity reaction such as Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated allergic reactions.
Replacement for trans fat in margarine:
Trans fats are not healthy and may have deleterious effect on the body. Since the production of margarine requires a solid fat, hydrogenation is used to harden vegetable oil in margarine making.
This hydrogenation generates trans unsaturated fatty acids, which are dangerous to the cardiovascular system even more than saturated fatty acids. Since shea butter is solid at room temperature, and has stearic acid as the main saturated fatty acid fraction, it eliminates trans unsaturated fatty acid.
Stearic acid is one of the healthiest saturated fatty acids. Also, unsaponified fraction of shea butter exhibit anti-hypercholesterolemic effects in animal studies (Malachi Oluwaseyi Israel, 2015)
Shear Butter Benefit to Skin:
Shear butter is used in skin care products such as lotions, creams, cosmetics preparations. Low quality shea butter is mixed with other oils, as a base when making soaps.
Sunscreen effect: Shea butter can absorb the ultraviolet radiation from the sun, protecting and serving as sunscreen to the skin. It protects the skin from sunburn, erythema, and skin cancers that could result from excessive sun rays.
The unsaponifiable fraction of shea butter has cinnamate esters of triterpene alcohol as the main constituent. The esters absorb UV radiation of the wavelength range 250-300 nm, and could serve as sunscreen and protect the skin from UV radiation in weather extremes (Nahm, 2011).
Skin healing effect:
Shea butter has anti-inflammatory effect, and healing properties. It has constituents such as fatty acids and plant sterols such oleic, palmitic, stearic and linoleic acids. This oil-soluble components do not undergo saponification, making it a good healing compound.
It contains vitamin A that soothes the skin, and prevent allergies, and vitamin F which rejuvenates and heals the skin.
Raw shea butter is used for scars, burns, stretch marks, skin rashes, irritation, keloids, eczema, insect bites, stings, arthritis, muscle fatigue, and as a skin disinfectant.
Skin emollient and moisturizing effect:
Shea butter has semi-solid and buttery consistency, coupled with vitamin A and E content. This makes it an excellent moisturizing and emollient substance for hair and skin.
The olein fraction is also used in creams or surfactant based products like bath products and shampoos to provide moisture to the skin, scalp, and hair.
Some desirable properties include being solid at room temperature, but melting at body’s temperature, good skin absorbability and water-binding properties. Shea butter is superior to mineral oil in preventing Trans-Epidermal Water Loss (TEWL).
Prevent skin ageing:
Shea butter has UV anti-erythemic activity, and prevent ageing of the skin. It also stimulates cell regeneration, and boost collagen production. Components such as α-amyrin and lupeol boost the skin collagen and elastin, and helps to prevent ageing and improve skin toughness, and elasticity.
Shea Butter Benefit to Hair
Shea butter protects the hair from harsh weather conditions, heat. It softens the hair, restores moisture, and rejuvenates brittle and damaged hairs. It has a non-greasy texture and spreads evenly in the scalp.
Furthermore, it can be beneficial in dandruff. There are many hair care products with shea butter, such as cantu curling cream.
References
- https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Vitellaria+paradoxa
- https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/234662463.pdf
- https://www.longdom.org/open-access-pdfs/shea-butter-an-opposite-replacement-for-trans-fat-in-margarine-2155-9600-S11-001.pdf
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277021242_Effects_of_Topical_and_Dietary_Use_of_Shea_Butter_on_Animals
- https://digitalscholarship.tnstate.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1000&context=biology_students