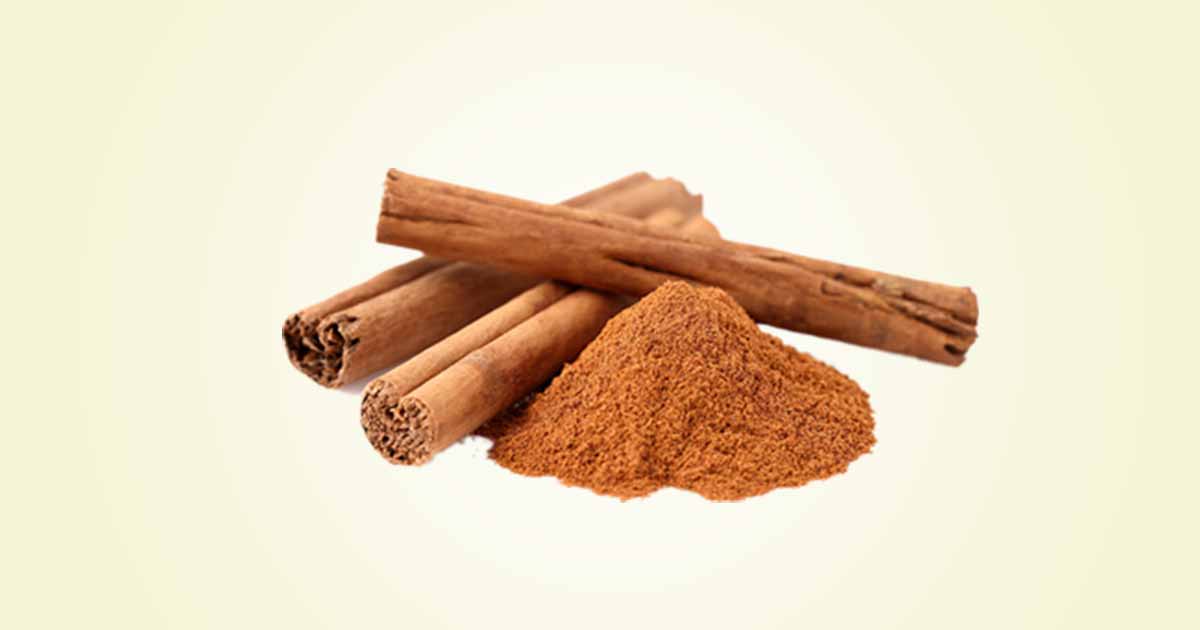
Cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum, or Cinnamomum verum), also called dalchini, true cinnamon, or Ceylon cinnamon, is a plant from the Lauraceae family. The part used for spice and herbal purposes is the bark. The inner back has more medicinal constituent and essential oils. The word, cinnamon, is from a Latin word meaning sweet wood.
Cinnamomum verum has astringent, carminative and stimulant properties, among other uses. Both the essential oil, the bark extracts, and powder extracts are utilized.
It is distributed in India, Sri Lanka, China, Brazil, Mauritius, Jamaica and other countries.
There are two main varieties, such as Cassia Cinnamon (Cinnamomum loureiroi, Cinnamomum aromaticum, Cinnamomum burmannii), and Cinnamomum verum. The Cinnamomum verum is also called pure, true, Mexican, Sri Lanka or Ceylon cinnamon and differs from cassia by the low levels of coumarins, and is more expensive. Also, coumarins are toxic to the liver when consumed in large doses.
The bark of the plant is used as a spice and flavoring in cooking but also in traditional and modern medicine. It is used to flavor chewing gums as it adds refreshing taste and also manage bad breath.
It is also used to flavor alcoholic beverages, and combined with sugar for flavoring cereals, bread-based dishes, such as toast, and fruits,
A tea, liqueurs, coffee or hot cocoa is made from the plant. The aromatic tea has sweet taste. Other products from cinnamon include leaf oil, bark oil, quills, powder, and chips.
Cinnamon has activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, neuroprotective, anticancer, gastroprotective, lipid-lowering, and prevents cardiovascular-diseases.
Home Remedy Uses of Cinnamon Powder
Cinnamon powder is used in home remedy for several conditions such as:
- Toothache, loss of taste, cold, and cough, insomnia, arthritis, memory boost: Using a mix of cinnamon and honey in different proportions.
- Influenza: Using a boiled mixture of cinnamon, clove, and ginger roots in water
- Bad breath, impaired digestion using the powder
- Diarrhea: Using it with sonth, cumin seeds and honey.
- Acne and pimple: The herb mixed with lemon juice.
- Hair fall: Cinnamon mixed with honey in warm olive oil applied to the scalp.
Composition
Cinnamon contains a group of resinous compounds such as cinnamaldehyde, cinnamate, cinnamic acid.
The essential oils include trans-cinnamaldehyde, cinnamyl acetate, eugenol, L-borneol, caryophyllene oxide, b-caryophyllene, L-bornyl acetate, E-nerolidol, 𝛼-cubebene, 𝛼-thujene, terpinolene, 𝛼-terpineol.
The root bark has mostly camphor, while the leaves and bark has mostly eugenol and cinnamaldehyde.
Nutritional Composition
According to USDA, a 100g of cinnamon spice contains 10.6 g of water, 53.1 g of dietary fiber, 80.6 g of carbohydrates, 3.99 g of proteins, 1.24 g of total lipids, 2.17 g of sugars, 247 kcal of energy.
There is high calcium (1000 mg), potassium (431 mg), magnesium (60 mg), phosphorus (64 mg), manganese (17.5 mg). Other minerals include iron, sodium, zinc, copper, and selenium.
Vitamin content include vitamin C, niacin, riboflavin, thiamine, folic acid, choline, betaine, Vitamin B-6, Pantothenic acid, vitamin A, vitamin E, vitamin K.
Health Benefits
Anti-inflammatory activity: Cinnamon and its essential oils are anti-inflammatory compounds. Flavonoids compounds such as gossypin, gnaphalin, quercetin, hesperidin, hibifolin, hypolaetin, oroxindin also have similar action.
It inhibits the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthesis (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and nitric oxide (NO) production in the central nervous system (CNS).
Antidiabetic action: Cinnamon lowers the blood glucose and cholesterol levels. Also, the polyphenol type-A polymers in cinnamon acts like insulin.
A newer compound from the hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives named naphthalenemethyl ester is antidiabetic.
Other compounds such as catechins, rutin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, and quercetin may be effective in glycemic control. It is marketed as a food supplement to control diabetes.
Antioxidant effect: Flavonoids and essential oils such as E-cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, and linalool has activity against hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide, and lipid peroxide free radicals.
Antioxidants are used in food industries to prevent spoilage. In human system, it prevents cardiovascular diseases, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases in humans.
Prevents Cancer: The plant extract inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor subtype 2 (VEGFR2) kinase activity, and angiogenesis. Cinnamaldehyde and its derivatives are antitumor compounds.
It can improve colon health and prevent colon cancer.
Prevents Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs): Flavonoids, and phenolic compounds such as epicatechin, catechin, and procyanidin B2 inhibits the formation of AGEs by trapping reactive carbonyl species. This may be an effective step in managing diabetes.
Prevents cardiovascular diseases: Cinnamaldehyde has hypotensive property, and cause vasodilation in animal studies. Compounds from the plant – cinnamic aldehyde and cinnamic acid may prevent myocardial ischemia.
Cinnamophilin is a thromboxane synthase inhibitor and TXA2 receptor antagonist. It has potential in the management of platelet aggregation, vascular diseases, atherosclerosis, and cancers.
Prevents neurodegenerative diseases: Some isolated compounds from the plant may prevent neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease (PD), and Alzheimer’s disease.
The mechanism may be reduction in formation of toxic 𝛽-amyloid polypeptide (A𝛽) oligomers, reduction in plaques and improvement in the cognitive performance.
Antimicrobial activity: Matan et al. reported antibacterial activity of cinnamon oil against Pediococcus halophilus, Staphylococcus aureus, fungi such as Aspergillus flavus, Mucor plumbeus, Penicillium roqueforti, and Eurotium sp, and yeasts such as Candida lipolytica, Pichia membranaefaciens, Debaryomyces hansenii, and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii.
Goni et al. reported that a combination of clove and cinnamon oils inhibit gram-positive bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus cereus, and gram-negative organisms such as Salmonella choleraesuis, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Yersinia enterocolitica.
It has more antimicrobial activity than neem (Azadirachta indica) and clove (Syzygium aromaticum)
Lipid lowering activity: The herb reduced the total cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoproteins in mice. Studies by Khan et al. suggest that consumption of 1,3, and 6 g of cinnamon could lower triglyceride, total cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol levels in humans.
Coagulant effect: Cinnamomum zeylanicum is a coagulant and prevents bleeding.
Antityrosinase activity: Cinnamaldehyde (E) has antityrosonase activity. This may be utilised in food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Tyrosinase inhibitors prevent hyperpigmentation and browning effects in mushrooms, fruits, and vegetables.
Drug Interaction
The cinnamon type, called cassia cinnamon, contains coumarin. Coumarin affect the function of drug metabolising enzymes CYP 2D6 and 3A4. Because of this, the cassia type may interact with anticoagulant, warfarin, and blood pressure lowering drugs like amlodipine, diltiazem, felodipine isradipine, metoprolol, nicardipine and nifedipine.
Also, cinnamaldehyde, a compound in the plant, inhibits the enzyme CYP 2A6. It may interact with metabolism of nicotine, especially in smokers.
Side Effects
Though true cinnamon has low levels of coumarins that are considered less harmful, the cassia type has high levels of coumarins, which can cause liver and kidney toxicity when consumed in large quantity.
Use in Pregnancy: The levels of cinnamaldehyde levels in cinnamon fprmulations such as the powder capsules possibly constitute a risk for pregnant women. Animal studies suggest it can cause harm to the unborn offspring.
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262229451_Cinnamon_A_Multifaceted_Medicinal_Plant
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171320/nutrients
- https://www.peoplespharmacy.com/articles/beware-interactions-between-cinnamon-and-medications
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338936717_Cinnamon_Cinnamomum_zeylanicum
- https://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2014/642942.pdf