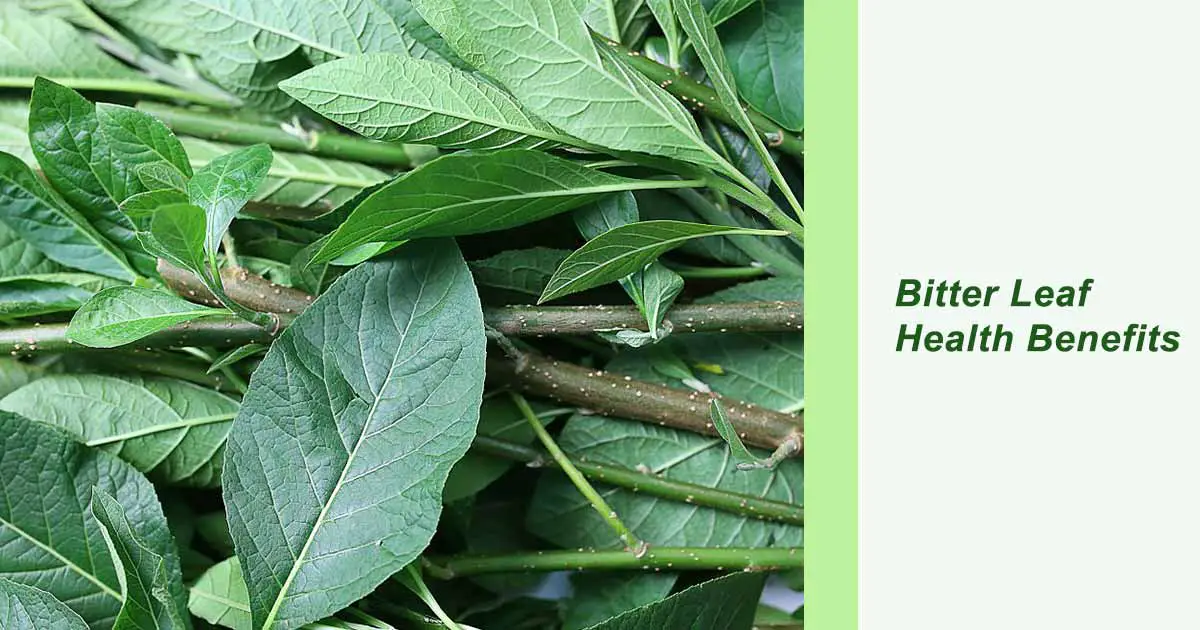
Vernonia amygdalina, popularly called bitter leaf, is a perennial herb or shrub that grows in the coastal savannah region. The edible vegetable from the Asteraceae family now grow in most part of Africa, and Asia. The difference between this plant and Vernonia colorata is the hairy leaves present in the latter. Vernonia genus has over 1000 species of plants, but bitter leaf is the most studied of them.
This wooded shrub grows up to 2 to 10 m, and does not produce seeds. The planting is by the stem. Vernonia amygdalina has an odor and bitter taste because of the saponins, alkaloids, tannins and glycosides. Because of this bitterness, they wash the plant numerous times while changing water. Boiling can reduce the bitter taste.
Bitter leaf plant has many constituents that are of health benefits. They have been utilised to treat various ailments traditionally. In Uganda, the powder is used to treat malaria. They use the decoction of the leaves and roots in traditional medicine to treat stomach disorders, fever, and kidney problems.
Apart from the health uses, bitter leaf can serve as vegetable for soup (onugbu in Nigeria, Ndole dish in Cameroon), wine (honey wine called Tei in Ethiopia is made from bitter leaf)
Bitter leaf has different names in various parts of Nigeria, such as Onugbu (Igbo), Ewuro (Yoruba), other Nigeria names are Etidot, Ityuna, Oriw, Chusa-doki, Shiwaka. Names in other countries are Ikaruga (China), Suwaaka (Cameroon), South Africa leaf (Malaysia), Ndoki (Gabon), Olulusia (Kenya), Omjunso (Tanzania), Awonoo, Awonwene, Jankpantire (Ghana), Grawa (Ethiopia), Omjunso (Tanzania).
Constituent of Vernonia amygdalina
Medicinal Constituent of Vernonia amygdalina
They have found some biologically active substances from the extract of bitter leaf. They are saponins, flavonoids, steroids, terpenes, alkaloids, , lignans, xanthones, anthraquinones, phenolics, triterpenoids, different sesquiterpene lactones.
Sesquiterpene lactone present are vernodalin, vernolepin, hydroxyvernolide, vernomygdin, vernolide, vernodalol, and epivernodalol. The steroidal glycosides isolated are Vernoniosides A1, A2, A3, B1, Vernoniosides D and E.
Flavonoids such as luteolin, luteolin 7-O-βglucuronoside and lutelin7-O-β-glucoside are got from the bitter leaf. These flavonoids protect the vitamins and enzymes and prevent fat oxidation. They are powerful antioxidants, and have other activities such as protection of the liver, prevention of cancer, inflammation, virus and bacteria.
Triterpenoids such as thiamine, pyridoxine, ascorbic acid, glycine, cysteine, eucalyptol, casein hydrolysate, beta piene, myrtenal, and alpha-muurolol can be found in stem, leaves, and roots. They have antibacterial, liver protection, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive effect.
Sesquiterpene lactones also exist in the leaves, stems and roots. Vernodalin and vernolide have more potent anticancer activity than hydroxyvernolide, vernolepin, vernomenin, and vernodalol. Vernolepin is an anti-platelet agent. Vernolide is active against gram-positive and negative bacteria such as S. aureus, Streptococcus pyrogens, B. subtilis, Salmonella pooni, Staphylococcus epidermidus.
Nutritional Content of Vernonia amygdalina
Apart from the phytochemical, the roots, leaves, and stems of Vernonia amygdalina have abundant nutritional content. The leaves contain proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, iodine, total oxalate, crude fiber, hydrocyanic acid, acids, amino acids (cysteine, glycine, casein hydrolysate), vitamins (pyridoxine, nicotinamide, thiamine, ascorbic acid) and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, iron, zinc, potassium. It contains low cyanide.
Vernonia amygdalina Health Benefits
Bitter leaf has many phytochemical that can be beneficial to health. An added advantage is the low toxicity of the plant. Some of them are:
1. Antidiabetic action: Diabetes leads to a high blood sugar level, which is detrimental to health. Studies show that the leaf extract of Vernonia amygdalina reduces sugar level, increase serum triglyceride levels.
A decoction of bitter leaf and neem plant reduces blood sugar level, so also is the combination of V. amygdalina Del and Gongronema latifolium. The anti-diabetic effect may be due to the many polyphenols in the extract.
2. May prevent leukemia: Root culture of cold, hot water or ethanolic extract of V. amygdalina may be beneficial to acute leukaemia and myeloid leukaemia patients.
3. Antifungal property: Vernodalol and vernolide, the sesquiterpene lactones in the V. amygdalina leaves extract have an antifungal action against Penicillium notatum, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus flavus.
4. Antibacterial activity: The water, ethanol, and methanol extract of bitter leaf has an antibacterial action against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus mutans, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Also, sesquiterpene lactones have action against gram-positive bacteria.
5. Effect on reproduction: Research with 95% ethanolic extracts of Vernonia amygdalina on mouse uterus led to a reduction in implantation sites, number of live foetus and survival.
6. Anti-inflammatory property: The leaf extract may have anti-inflammatory action. The root extract also has this activity, but not at the same level as the leaves. In traditional medicine, they apply the raw extract on wound to improve healing.
7. Antioxidants: Flavonoids in the V. amygdalina have antioxidant property. Consuming bitter leaf may increase the levels of antioxidants, such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione, and malondialdehyde in the body.
Antioxidants scavenge the free radicals that cause oxidative stress and diseases in the body and also detoxify the body.
8. May prevent cancer: V. amygdalina leaf extract may inhibit the spread of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 associated with breast cancer. Epivernodalol, a methanolic extract, may prevent skin melanoma, a serious skin cancer.
9. Anti-malarial action: Experimental on laboratory mice showed that the leaves and root extract have anti-plasmodial activity against Plasmodium berghei. Also, sesquiterpene lactones have an antimalarial action against Plasmodium falciparum.
10. May prevent allergy, such as atopic or eczema dermatitis syndrome
11. Immune boasting: Antioxidants such as saponins, tannins, and flavonoids may improve CD4+ cells. This may also be due to early release and maturation of leucocytes.
12. Antihelmintic: Acetone extract may inhibit nematode eggs and nematode larvae (Haemonchus contortus, Trichostrongylus spp., Strongyloides)
13. Fertility: Experiment on male Wistar rats using bitter leaf extract showed improved sperm motility and concentration.
Other medical uses of the bitter leaf plant are in treating stomach disorder, purging, worm infestation, constipation, kidney problems, cough, and to manage obesity.
How to Make Bitter Leaf Juice Extract
Bitter leaf is used to make soups, but they can also convert the leaves into juice. Drinking the juice is believed to be beneficial to the health in many ways. To make this:
- Wash the bitter leaves with clean water.
- Squeeze and macerate the leaves in a bowl of water. Repeat the process to extract the constituent from the plant.
- Add a fresh cup of water as you squeeze out the juice.
- Sieve out the juice from the marc.
Bitter leaf and garlic
Bitter leaf and garlic juice mixed together may help to prevent high blood pressure, heart diseases. Both plants also aid digestion and treat digestive ailments, cough. Other health benefits are anticancer, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic properties.
Bitter leaf and milk
Milk, garlic, or honey can be added to bitter leaf juice. Milk contains the vitamins A, D, E and K, a small quantity of B complex and C, minerals such as chlorides, phosphates and citrates of sodium, calcium and magnesium. Proteins such as casein, whey protein abounds.
Adding milk to bitter leaf helps to mask the bitter taste while also supplying nutrients to the body. The milk also supplements the numerous health benefits of the bitter leaf.
Toxicity and Side Effects of Bitter Leaf
Vernonia amygdalina is safe and does not appear to be toxic. The only observed side effect of Vernonia amygdalina is the decrease in red blood cell count. At certain doses, it may increase serum bilirubin.
Can I drink bitter leaf juice on an empty stomach?
Taking bitter leaf juice on an empty stomach may boost the metabolic rate by 30%. Increased metabolism in the body prevents weight loss, lowers the risk of diabetes, blood pressure, hypercholesteremia. It may also improve fertility, immunity, liver function, bowel movement.
Does bitter leaf help sexually?
Bitter leaf could increase glucose metabolism, which helps to create pyruvate. Pyruvate is a substrate that helps in movement and survival of sperm cells. A study on rat suggests bitter leaf extract may improve sperm motility, survival, morphology and concentration due to the antioxidants, flavonoids, vitamin content.
References: