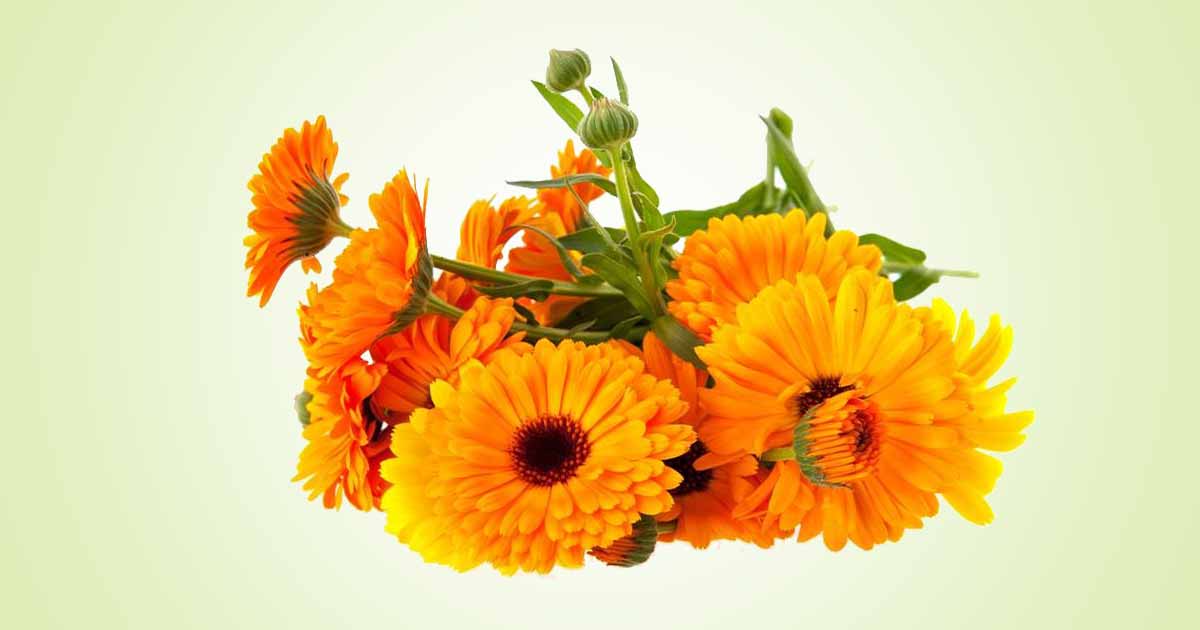
Calendula officinalis, or Marigolds, is an annual edible herb belonging to the Asteraceae family, alongside asters, chrysanthemums, sunflowers. It is notable for the colorful flowers. Pot marigold is native to Eurasia, and is used for horticulture and in traditional medicine. In the spice trade, pot marigold is used as an inexpensive substitute to saffron.
Calendula officinalis comes from the Latin term “calends”, which is the first day of the month the flower grows. Calendula is also called “herb of the sun” due to the flower’s efflorescence in the morning, and shrivelling in the evening.
Other names of marigold include calendula (pot marigold), calendula, English marigold, common marigold, garden marigold, gold bloom, holligold, marigold, Mary bud, ruddles. Marigold is grown in the Mediterranean, Germany, Australia, Czech, Austria, Switzerland, Hungary, Egypt, and Syria.
The Calendula genus has many species, but the most important ones include C. officinalis, C. arvensis, C. tripterocarpa, C. stellata, and C. suffruticos. Calendula officinalis is the most utilized and studied marigold species.
Calendula officinalis is a self-seeding annual plant that can grow up to 18 inches (0.46 m). It has a composite flower head rests on the plant’s stem.
The aromatic leaves are green, simple, lanceolate, oblong, and obovate-shaped, with dentate leaf margin. The stem is straight, sparsely branched lax or erect. The fruit is an achene.
The edible flower can be orange, red, gold to yellow. It has a single to double flowerheads, with possible contrasting darker center disks. The flower petals give color to custard, soups, and rice, and can also be used in cookies, vinegar.
Pot marigold is also used to produce creams, shampoos, lotions, deodorants, and toothpastes. The Calendula oil is approved by the European Medicines Agency as a herbal medicine to treat minor burns, wounds, and skin problems. Current Calendula formulations include pot marigold tincture and carophyllenic ointment, with carotenoids content. The powder is a yellowish-brown powder with a distinctive aromatic smell and a mildly bitter taste.
Calendula officinalis has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, antihelminthic, antidiabetic, wound healing, hepatoprotective, and insecticidal activities. It can be used to treat dermatitis, and is comparable to aloe vera.
Composition of Calendula officinalis
The flowers and leaves of marigold contain triterpenes, flavonoids, phenolic compounds (chlorogenic acid, tannins, rutin, narcissin and quercetin), carotenoids, resins, albumins, and hydroxycoumarins and essential oil (Fernandes et al., 2013; Gazim et al., 2007). The seed fat contains calendic acid. The root extract contains inolin.
- Carbohydrates: polysaccharides, monosaccharides.
- Amino acids: alanine, arginine, aspartic acid, aspargine, valine, histidine, glutamic acid, leucine, lysine, proline, serine, tyrosine, threonine, methionine and phenylalanine.
- Lipids: phospholipids, glycolipids, esters such as lauric, myristic, palmitic, stearic, oleic, linoleic and linolenic acid. The seed contains trienic, dimorphecolic, and octadecadienoic acids.
- Flavonoids: quercetin, isorhamnetin, isoquercetin, isorhamnetin-3-O-β-D-glycoside, narcissin, calendoflaside, calendoflavoside, calendoflavobioside, rutin, isoquercitrin.
- Carotenoids: neoxanthin, violaxanthin, luteoxanthin, α-cryptoxanthin, β-cryptoxanthin, lycopene, α-carotene, z-cryptoxanthin, β-carotene, mutatoxanthin, flavoxanthin, auroxanthin, antheraxanthin.
- Terpenoids: sitosterols, calendulaglycosides, calendulosides, glucosides of oleanolic acid and glucuronides, cornulacic acid acetate, diesters of diols, 3-monoesters of taraxasterol, ψ-taraxasterol, lupeol, erythrodiol, brein, ursadiol
- Coumarins: scopoletin, umbelliferone and esculetin
- Quinones: phylloquinone, α-tocopherol, ubiquinone, phylloquinone, α-tocopherol
- Bitter constituents like loliolide (calendin), calendulin, and n-paraffins
- Volatile compounds: β-pienene, limonene, 1,8-cineol, p-cymene, α-thujene, α-pienene, sabinene, trans-β-ocimene, γ-terpenene, δ-3-carene, nonanal, terpene-4-ol, 3-cylohexene-1-ol, α-phellandrene, α-terpeneol, geraniol, cadinene, nerolidol, α-ylangene, α-humulene, endobourbonene, oplopenone, α-cadinol, caryophyllene, α-ylangene, carvacrol, bornyl acetate, sabinyl acetate, cubebene, α-copaene, α-bourbonene,
Medicinal Benefits of Marigold (Calendula officinalis)
Marigold has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory actions, antimicrobial, healing, emollient, and dental effect.
Antioxidant activity:
Orange flowers of Calendula officinalis contain more antioxidants than the yellow flowers. Extract from the petal also showed more antioxidant activity than the flower extract. Flavonoids, flavoxanthin and auroxanthin, carotenoids, mostly lutein, and zeaxanthin, and beta-carotene are the major antioxidant compounds.
Antioxidant compounds help to prevent heart disease, malaria, diabetes, stroke, cancer, and arteriosclerosis.
Anti-inflammatory activity:
Calendula officinalis contains the anti-inflammatory compound and antiedematous compounds such as oleanane-type triterpene glycoside, and esters of faradiol-myristic acid, faradiol-palmitic acid and ψ-taraxasterol.
Marigold extract inhibits edema in croton oil-induced mouse. A cream formulation with calendula extract is reported to be effective in dextran and burn edemas and in acute lymphoedema in rats.
The herbal preparation is used for symptomatic treatment of minor inflammations in the mouth or the throat. A homeopathic drug, Traumeel®, used to relieve the pain and swelling caused by sudden musculoskeletal injuries, contains Calendula.
Antimicrobial activity:
Extract from the flower of marigold inhibit periodontal bacteria such as Porphyromonos gingivalis, Prevotella spp., Furobacterium nucleatum, Caphocytophaga gingivalis, Veilonella parvula, Eikenella corrodens, Peptostreptococcus micros and Actinomyces odontolyticus. This explains the use of the plant extract in dental products like toothpaste, mouth washes to treat gingival inflammation.
The essential oils also showed good antifungal activities against Candida albicans, Candida dubliniensis, Candida parapsilosis, Candida glabrata, Candida tropicalis, Candida guilliermondii, Candida krusei, and Rhodotorella spp.
The flower tincture showed in vivo antiviral activity against herpes simplex, influenza A2 and influenza APR-8 viruses.
Anthelmintic activity:
Extract of Calendula has anthelminthic activity against adult Indian earthworms, Pheretima posthuma, and against Ascaris suum, and larvae of Strongiloides papillosus.
Antiprotozoal activity:
A novel compound in Calendula, 6Z,9Z)-heptadeca-6,9-diene-5,11-dione, has a mild antitrypanosomal activity, and leishmanicidal activity against L. donovani amastigote and ecdysone.
Anticancer effect:
Isolated compound from pot marigold, calenduloside F6′-O-n-butyl ester, exhibit cytotoxicity against leukemia, colon cancer, and melanoma. Aqueous laser-activated calendula flower extract (LACE) inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells in human and murine tumour cell. LACE exhibit in vitro induction of proliferation and activation of B-lymphocytes, CD4+, T lymphocytes and NKT lymphocyte.
The saponin constituent also inhibits Ehrlich mouse carcinoma model.
Hepatoprotective effect:
In carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induced hepatic injury in Wistar rats, the flower extract reduce hepatic injury. It also reduced glutamo-oxalate-transaminase (GOT), glutamo-pyruvate-transaminase (GPT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), succinate dehydrogenase (SDH), cytochromoxidase (Cyox), and Mg2+ dependant adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase).
Markers of liver damage such as alkaline phosphatase, alanine and aspartate transaminase decreased significantly. The plant extract also inhibit human liver cancer cells.
Wound healing effect:
In induced thermal burns in rats, the flower of pot marigold extracts promoted wound healing by increasing the collagen-hydroxyproline and hexosamine contents. There was decrease in lipid peroxidation, and level of acute phase proteins (heptaglobin, orosomycid and tissue damage marker enzymes).
Herbal formulation of Calendula has been used for minor wound healing, and reduce pain, redness, and swelling.
Cardiovascular activities:
Calendula officinalis extract exhibited cardioprotective effect in rats by stimulating left ventricular developed pressure and aortic flow, as well as by reducing myocardial infarct size and cardiomyocytes apoptosis. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect is responsible for protection against ischemic heart disease.
Immunostimulatory effect:
Polysaccharides, especially Polysaccharide III from marigold extract, exhibited phagocytosis when tested during an in vitro granulocyte test.
Insect repellant effect:
Calendula has a pungent odor and can be an effective pesticide and insect repellant against white flies, and milkweedbug.
Sedative effect:
Ingestion of Calendula preparation could lead to sedative effect, with the effect further increased when combined with sedative agents. Calendula increased hexobarbital induced sleeping time in rats. However, the topical application did not cause such effect.
Anti-HIV activity:
Extract of the flowers inhibited the replication of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase activity, in acutely infected lymphocytic MOLT-4 cells in vitro.
Cosmetic use:
Marigold contains saponins, resins, and essential oils that are used in cosmetic preparations to treat dermatitis, inflammation, wounds. Calendula ointment can serve as adjuvant therapy for acute dermatitis during irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer.
Contraindication
People with allergic reaction to Asteraceae (daisy) plants.
Since there is fewer data on safety during pregnancy and lactation, Calendula officinalis should be avoided in such situations. Also, use in children under 6 years is not recommended.
References
- https://plants.ces.ncsu.edu/plants/calendula-officinalis/
- https://gobotany.nativeplanttrust.org/species/calendula/officinalis/
- https://www.academiapublishing.org/print/Fonseca%20et%20al.pdf
- https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-monograph/final-european-union-herbal-monograph-calendula-officinalis-l-flos-revision-1_en.pdf
- https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/16/4/611
- https://gardenerspath.com/plants/flowers/pot-marigold/
- http://medcraveonline.com/PPIJ/PPIJ-06-00171.pdf
- https://www.ajol.info/index.php/tjpr/article/view/48090/34455
- https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=af5d27c1499def5f2d27332f6e80ce6cb66d7ad0