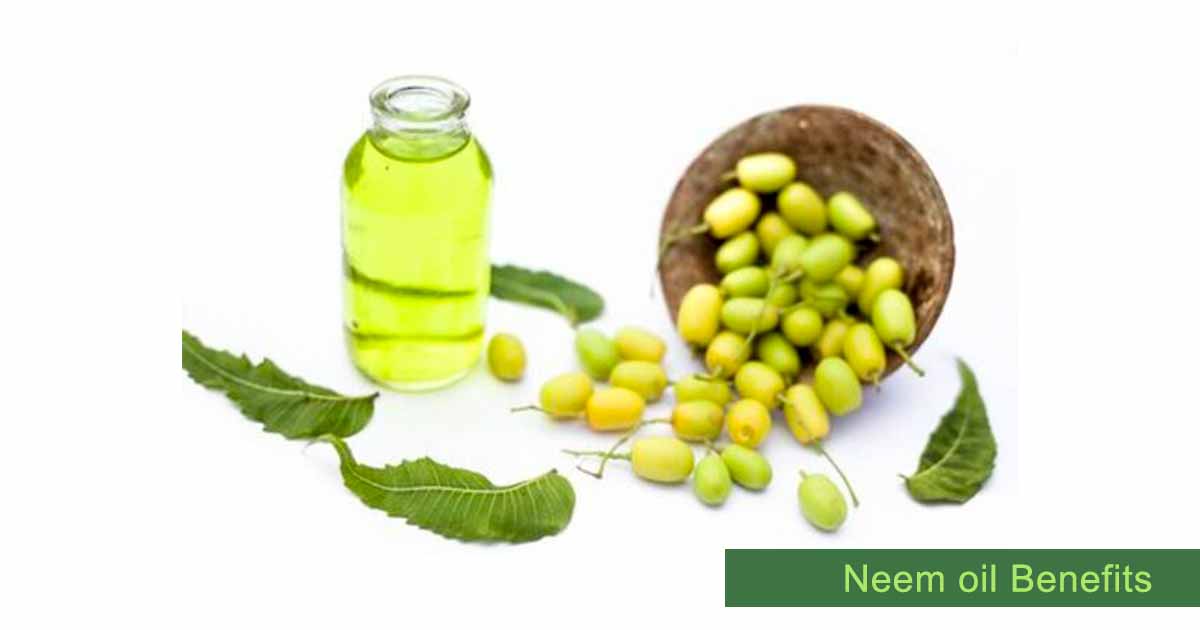
Neem, Azadirachta indica, belongs to the family, Meliaceae. It is originally from India but now grows in other tropical and subtropical region. Neem oil is a natural byproduct of neem. Countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, Nepal, Thailand, Vietnam, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, England, France now plant neem tree.
The tree is an evergreen, small to medium-sized with the height between 15 to 30m. Leaves are glabrous, light green, and long. The bark is thick, dark gray to red color, with gummy colorless sap. Flowers are sweet smelling, small sized, white or pale yellow. Fruits are also small, greenish to yellow.
Neem oil
The leaves, fruit and seed are sources of neem oil. The seed kernel is the most used for preparing neem essential oil, and it can yield as high as 45% of oil. Three methods: mechanical pressing, solvent extraction and supercritical fluid extraction are used in extracting the oil.
The mechanical pressing (cold pressing or temperature-controlled pressing) is the most used method that can yield 90% of oil, but the oil has low quality due to low azadirachtin content. It is turbid, has water and metal content.
Solvent extraction is preferable to the mechanical pressing because of the quality of the oil and the yield. Hexane, ethanol, ethanol–hexane mixtures are the solvent used.
Supercritical fluid extraction, an expensive method, helps to yield an oil of high quality, with no solvent residues. It uses supercritical CO2 (SC-CO2).
Neem oil is golden yellow, reddish-brown, greenish-brown, yellowish-brown, dark brown, or bright red liquid. It has an unpleasant and strong odor due to sulphur compounds. It is hydrophobic, non drying oil with a pungent taste.
Constituent of Neem Oil
Azadirachtins is the most studied constituent, and most active component of the neem. Azadirachtin A is the most potent of all azadirachtin. The constituent has insecticidal and pesticidal property. Nimbin, nimbinin, and nimbidin are the bitter principle in the plant.
Other constituents are nimolicinol, gedunin, nimbidiol. The flower oil has fatty acids such as linoleic, linolenic, palmitic, oleic, arachidonic, and docosatrienoic acids.
Hydrocarbon from the leaf oil is germacrene D, β-elemene, caryophyllene, γ-elemene while the flower oil has pentacosane, β-germacrene, tetracosane, β-caryophyllene, etc.
Neem seed oil has sterols such as β-sitosterol, campesterol, fucosterol, stigmasterol. α-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol are the main tocopherols.
Neem oil for hair
Neem oil contains phytochemical such as limonoids, triglycerides, fatty acids, vitamin E, and calcium that are good for hair growth and development.
Hair growth: Antioxidants and vitamin E in the oil help to improve skin regeneration, healthier scalp, and hair.
Hair lice: A research observed that neem seed extract killed head lice larvae after 5 minutes, and adult head lice after 10 minutes. Azadirachtins, especially Azadirachtin A, may be the constituent because of the insecticidal, and pesticidal action.
To apply neem oil to the hair or scalp, it is advisable to use the diluted form, as the raw form can cause irritation. Dilute with either of these carrier oils: coconut oil, olive oil in the ratio of one ounce of oil for every 12 drops of neem oil.
For safety, conduct a patch test on the skin to be sure your skin can the tolerate the topical formulation. To do this, apply the oil inside your forearm, cover with a bandage for 24 hours. If you experience any skin reaction, irritation, do not use the oil. If no reaction, you can continue using the oil.
Apply the oil to your scalp and allow for 1 to 2 hours daily. Leaving it for 24 hours may result in irritation.
Neem oil for skin
Neem oil contains constituents that are favorable to the skin. Skin care products with neem may treat acne, wounds, scars, psoriasis, eczema, and warts, and stimulate collagen production. The oil may help in wound healing. A study on rat shows that it may relieve aging symptoms such as wrinkles, dryness.
Dandruff: Neem plant contains anti-inflammatory agent nimbidin, which may help treat conditions such as psoriasis, scalp irritation, dermatitis. Dandruff’s primary causes are the yeast-like fungi – Candida and Malassezia, skin irritation, eczema, contact dermatitis.
The antifungal property of the oil can help balance the PH of the scalp, prevent skin irritation and dandruff.
Other uses of neem oil are for treating diseases such as chronic ulcer, eczema, epilepsy, intestinal helminthiasis, syphilis, and other inflammatory, arthritic, bacterial, viral infection.
Neem oil is an effective pesticide and essential-oil based insecticide. They are inexpensive, biodegradable, less toxic.
Is neem oil toxic to humans?
There have been reports of neem oil poisoning in children. It resulted in vomiting, hepatic toxicity, recurrent generalized seizures, leukocytosis, symptoms of Reye’s syndrome, metabolic acidosis, and encephalopathy. In another report, 10 children out of 12 died after single doses of neem oil with features of toxic encephalopathy and metabolic acidosis.
Neem pesticide injection by an adult caused encephalopathy and metabolic acidosis. There is no specific antidote for neem oil poisoning. Azadirachtin irritates the eyes, stomach, skin.