Oxygen mask is one of the oxygen delivery system to supply supplementary oxygen in patients with respiratory need. It covers the nose and mouth. An elastic band wraps around the back of the head and helps the oxygen mask stay attached. There is an oxygen tube in the lower front of the mask, and it connects to the oxygen source. Side ports are located near the cheeks of the mask, and it allows air from the room inside the mask while preventing carbon-dioxide build up in the mask.
An oxygen delivery system is used to administer, regulate and supplement oxygen to increase arterial oxygenation. This is used in acute oxygen therapy (respiratory distress, hypotension, acute hypoxemia, cardiac and respiratory arrest, low cardiac output + metabolic acidosis) and long term oxygen therapy.
Normally, oxygen masks are not used for long-term treatment, unlike nasal cannula.
Advantage of Oxygen Mask
- It has a higher flow rate of 6 and 10 liters when compared with nasal cannula
- The flow of oxygen is consistent
Disadvantages of Oxygen Mask
- It is difficult to speak or communicate while wearing the mask
- Can cause a feeling of claustrophobia in some patients
- Difficult to eat or drink
- Mask or elastic strap may be uncomfortable
- The mask must operate at a minimal flow rate to help flush out exhaled carbon dioxide.
Types of Oxygen Mask
There are different types of oxygen mask such as simple oxygen mask which provide low flow oxygen flow rates. There are other ones that deliver high oxygen concentration, such as partial rebreather or non-rebreather mask.
The oxygen masks can be for pediatric or adult use.
Different types of oxygen ranging from face mask, from simple mask to reservoir masks types. They include:
- Simple oxygen mask
- Partial rebreathing mask (reservoir type)
- Non rebreathing mask (reservoir type)
- Venturi mask
- Capnography mask
- Procedural oxygen mask
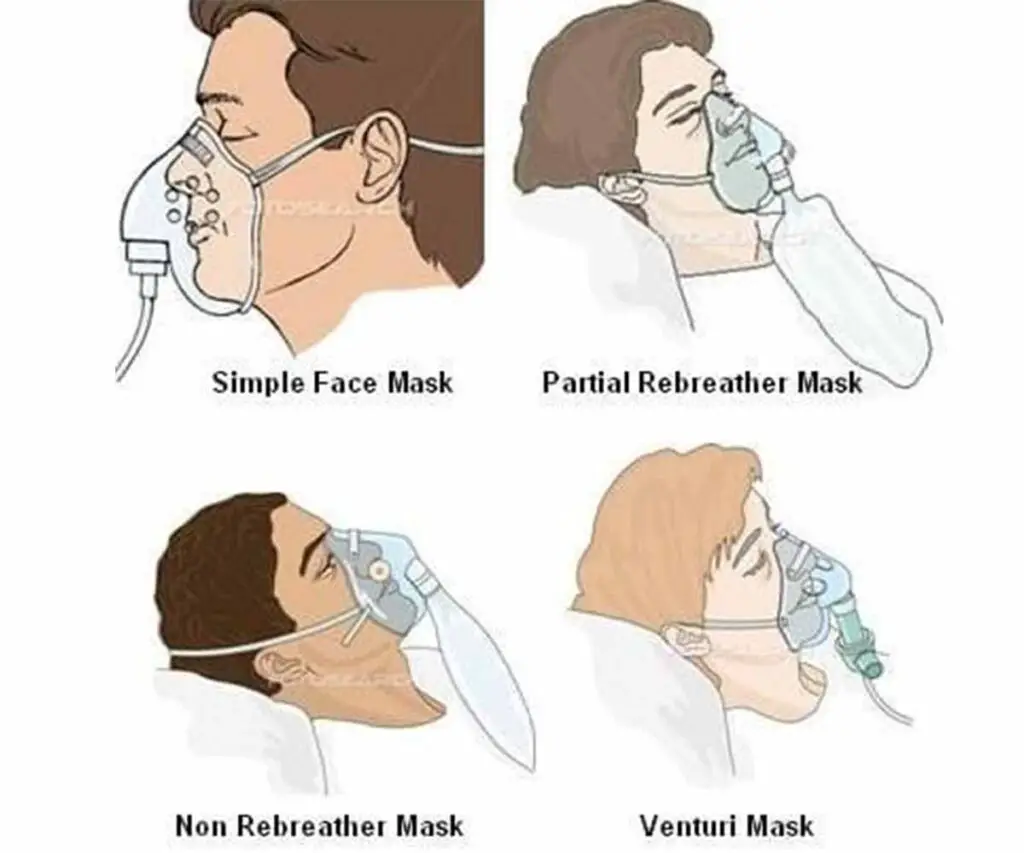
Simple Oxygen Mask
It is a transparent mask with side holes. It has a capacity of 100–250 ml. Different flow rate result in variable FiO2. Rebreathing of CO2 may occur when the flow rate of oxygen is 2L per minute, or when the minute ventilation is high.
When there is normal respiration, 4 L/min of oxygen flow delivers an FiO2 of about 0.35–0.4. Also, 8L/min flow rate do not increase FiO2. Simple oxygen mask deliver oxygen concentration of 35% to 55%.
- Advantages: It is less expensive
- Less intrusive than other types
- Provide low concentration of oxygen
- Used in mouth breathers
- Comfortable to wear for a long time.
- Can be used at home or hospital setting.
- Disadvantages: It may be uncomfortable
- Interfere with eating, drinking, and talking
- Does not deliver enough FiO2
- High chances of rebreathing
- The levels of FiO2 depends on the breathing effort.
Partial Rebreathing mask
It is a mask with the capacity of 1 liter, with the oxygen flowing directly into the reservoir and filling it during exhalation.
The design contains a one-way valve between the mask and oxygen reservoir. It allows some exhaled air to be breathed in again. One-third of the air you exhale goes back into the bag, and the other two-thirds vents into the atmosphere.
The FiO2 delivery is between 0.6 and 0.8. A minimum flow rate of 8L per minute is needed to remove exhaled CO2 and also refill the oxygen reservoir. The flow rate should be sufficient to keep the bag one-third or one-half inflated all the time.
Partial rebreathing mask is useful when oxygen supply is limited.
- Advantages: The inspired gas does not mix with the air in the room
- If the oxygen supply has issues, patient can breathe the room air through exhalation ports
- Deliver high oxygen concentration up to 50% to 70% in patients with breathing difficulty
- Disadvantages: Interfere with eating and drinking
- Increased oxygen flow does not increase the FiO2
- Must be used in a hospital environment.
Non Rebreathing Mask
Contains one-way valves between mask and bag, and exhalation ports. With a flow rate of 10 to 15 L, FiO2 of 95% can be achieved. It requires high oxygen supply rates, and you do not breathe in what you exhale.
This type is designed not to allow entrainment of air, but to avoid any of such, one out of the two exhalation ports is not provided with valve.
This mask needs high level of oxygen supplies. It is ideal in situations such as head injury where rebreathing of CO2 would be dangerous.
To achieve better results, adequate flow rates should be maintained so that the reservoir bag does not empty by more than one-third during inspiration. Using the best seal between the mask and the face is necessary.
A non-breathing mask delivers oxygen therapy concentration of 70% to 100%, and is used in situations such as trauma, smoke inhalation, cluster headaches, carbon monoxide poisoning, and airway restriction.
- Advantages: Highest possible FiO2 without intubation
- Ideal for spontaneously breathing patients with severe hypoxia
- Though used mostly in hospitals, it can be used at home with proper oxygen equipment.
- Disadvantages: It is costly
- Not ideal for long term use
- Interfere with talking or eating
- Requires tight seal, and may be uncomfortable
- Malfunction may cause the build up of CO2 and suffocation
- Requires a professional to fix it properly to work
Venturi Mask
Venturi mask deliver fixed level of oxygen concentration. The size of constriction determines the oxygen concentration in the flow. Increase in forward flow of inspired gas causes entrainment of gas.
The FiO2 can be 0.24, 0.28, 0.31, 0.35, 0.4 or 0.6. There is no rebreathing or increase in dead spaces as the exhaled gases are rapidly flushed from the mask, via its holes. This is because of the high fresh gas flow rate.
Venturi mask is recommended for patients whose ventilation depends on the hypoxic drive, and fixed oxygen concentration is necessary.
- Advantages: The FiO2 has fixed flow, is more reliable, and precise
- Help to decide if the oxygen demand is increasing or decreasing
- It saves oxygen cost due to high flow
- Disadvantages: It is uncomfortable
- Interfere with eating and drinking
- It is costly
- May not deliver high FiO2
Capnography Mask
Capnography masks are used in hospitals for oxygen therapy. A capnography mask oxygen therapy device covers the patient nose and mouth, and is attached to the tank. The oxygen mask regulates the oxygen flow to the mask, while the monitor measures the amount of carbon dioxide in the exhaled breath of the patient. It has a small tube that connects to the patient’s nose and to a monitor.
The measured amount of carbon dioxide in the capnography mask will help in adjusting the oxygen flow rate, and give the right quantity of oxygen.
Procedural Oxygen Mask
Procedural oxygen mask (POM) is an FDA-approved mask for procedural sedation and delivers 80% to 90% FiO2. This type of capnography mask is used in procedures such as bronchoscopy, conscious sedation, endoscopy, and other procedures.
POM has dual membranes for oral and nasal probes, and allow for inserting of probes, scopes, and tubes through the mask without obstructing their view.
It helps to supply high oxygen rate, and monitoring to improve safety.
References: